Figure 1. Possible mechanisms for maximal inflammatory responses elicited by LPS during hypoxia.
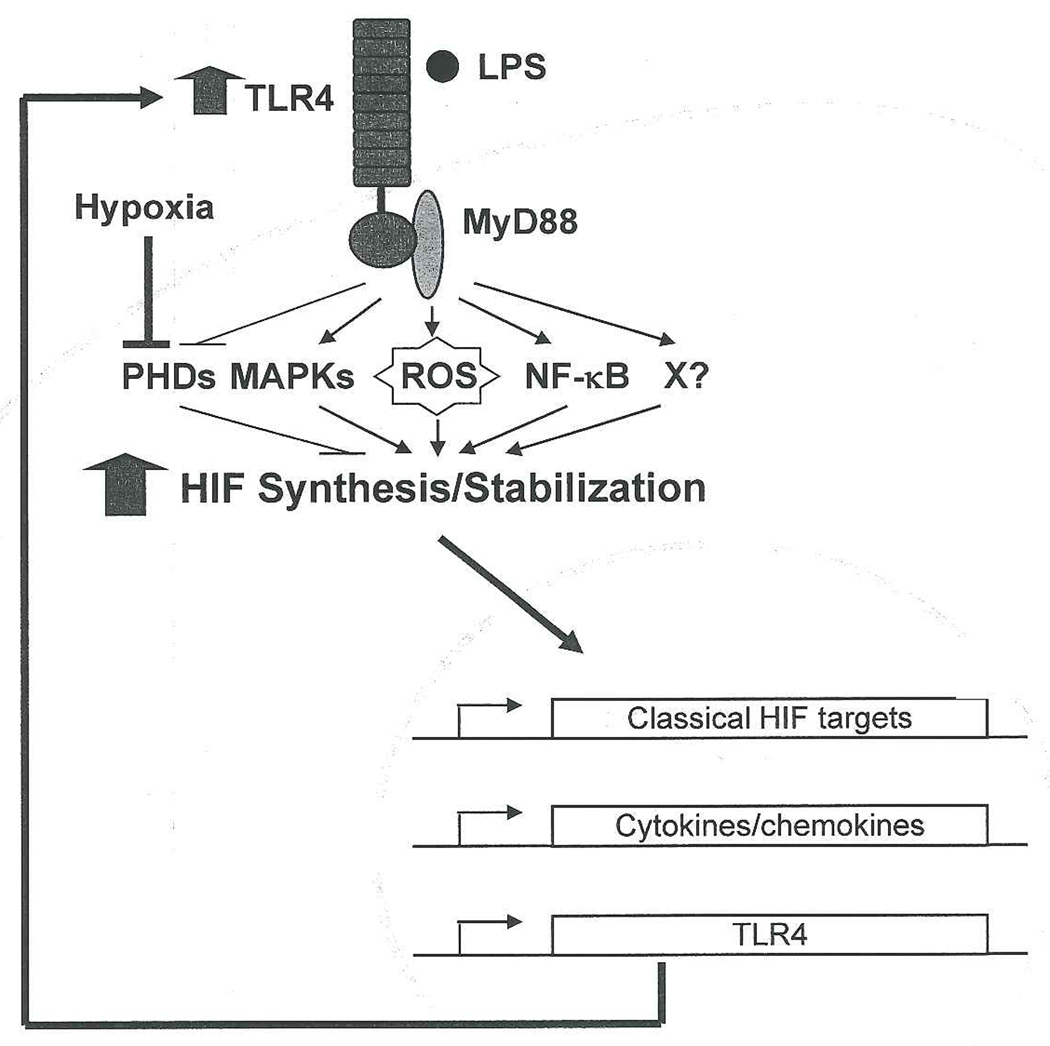
In macrophages, LPS induces HIF protein synthesis and stabilization in a TLR4/MyD88-dependent fashion. The signaling pathways for LPS-induced HIF stabilization possibly involve ROS, inhibition of PHDs, MAPK, NF-κB and/or unknown factors (X). Upon HIF protein accumulation, it translocates to the nucleus and stimulates expression of classical HIF target genes, inflammatory cytokines/chemokines, and TLR4. TLR4 further enhances HIF expression and transcriptional activity, resulting in a positive feedback loop. Together with the LPS-TLR4 pathway, hypoxia itself stabilizes HIF protein via inhibiting PHDs, serving to amplify HIF-mediated inflammatory responses during infection and O2 deprivation.
