Figure 1.
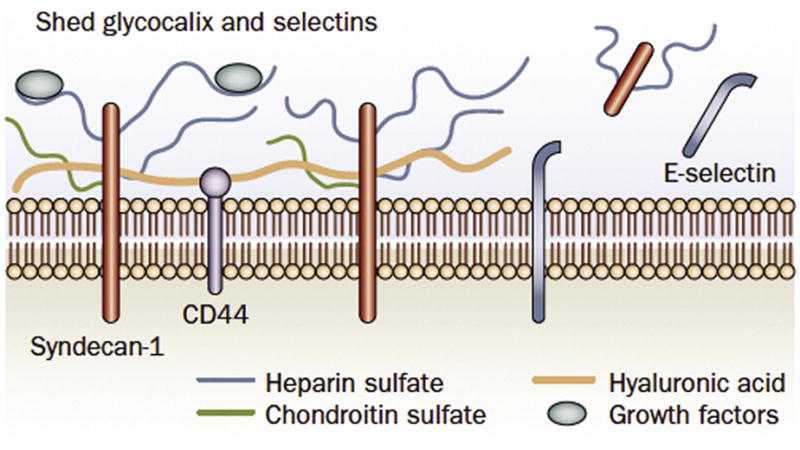
The glycocalyx contains anchoring proteoglycans (e.g. syndecan 1 and CD44) and connecting glycosoaminoglycans (e.g. heparan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid). The negative charge of the proteins constitutes an important charge barrier against filtration of albumin. During endothelial activation, the glycocalyx is modified to allow leukocytes and platelets to interact with the endothelial surface. Glycocalyx components are then modified and released into the circulation. With prolonged activation and early apoptotic events, adhesion molecules such as E-selectin may also be shed. (Reprinted by permission from Nature review Nephrology).
