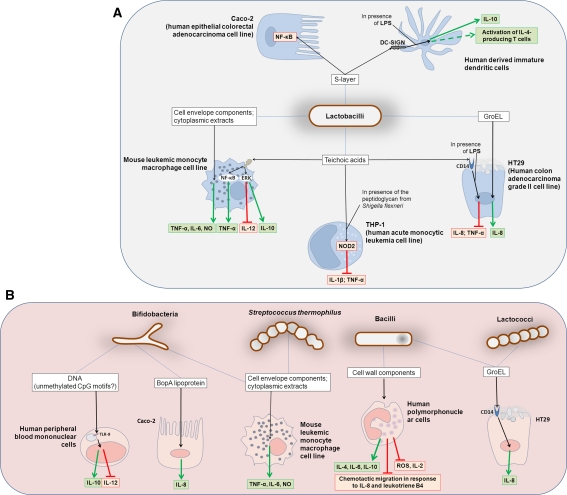
Fig. 1.
Interaction between host immune system and cellular components of probiotic bacteria. a Molecules or fractions from Lactobacillus cells demonstrated to activate host immune and epithelial cells. b Immunomodulatory molecules or fractions isolated from other probiotic bacterial cells. Cytokines, immunological activities or cell factors that have been inhibited are indicated in a red rectangle, while those that have been enhanced are in a green rectangle. The immunomodulatory activities shown in the picture have been experimentally proven only for certain strains/species inside a bacterial group: consult the references cited in the article for more details. GroEL is a chaperone protein (heat-shock protein) found in many bacteria; BopA is a cell surface lipoprotein identified in Bifidobacterium bifidum, which has been demonstrated to promote the adhesion of the bacterium on Caco-2 cells. DC-SIGN dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3-grabbing non-integrin, ERK extracellular-signal-regulated kinase, IL interleukin, LPS lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli, NF-κB nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells, NO nitric oxide, NOD2 nucleotide-binding oligomerisation domain containing, ROS reactive oxygen species, TLR Toll-like receptor, TNF-α tumour necrosis factor-α