Figure 6.
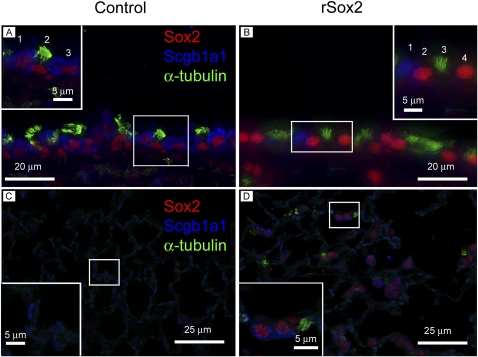
Sox2-expressing cells in conducting airway lack differentiation markers. Expression of airway differentiation markers was determined in bronchiolar (A, B) and alveolar epithelium (C, D) from control (A, C) and rSox2 mice (B, D) after 6 months of doxycycline treatment. Triple immunofluorescence for Sox2, Scgb1a1, and α-tubulin demonstrated that high levels of Sox2 in bronchiolar epithelium was associated with the absence of expression of Clara cell (Scgb1a1) or ciliated (α-tubulin) markers (B, inset). High levels of Sox2 seen in (B) precluded observation of lower Sox2 levels in Scgb1a1-positive and α-tubulin–positive cells in the bronchioles of rSox2 mice. In contrast, (Sox2+, Scgb1a1+) and (Sox2+, α-tubulin+) cells were observed in control mice (A, inset). In the alveolar epithelium of rSox2 mice, most Sox2+ cells were Scgb1a1+ and α-tubulin−, whereas some Sox2+ cells were Scgb1a1− and α-tubulin+ (D). Scgb1a1 expression in the alveolar epithelium of rSox2 mice (D) was weaker than in bronchioles (A, B).