Figure 2.
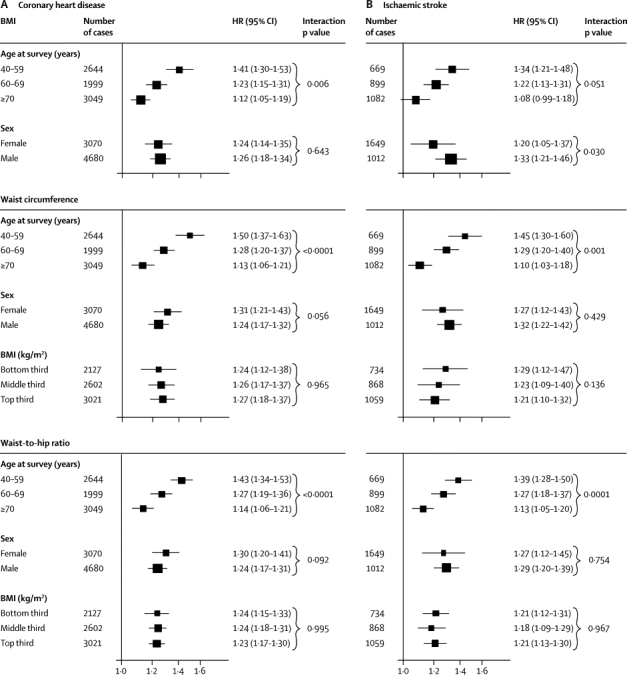
HRs for coronary heart disease (A) and ischaemic stroke (B) per 1 SD higher baseline values of BMI, waist circumference, and waist-to-hip ratio, according to age, sex, and BMI at baseline
Analyses for coronary heart disease were based on up to 203 338 participants from 51 studies, and analyses for ischaemic stroke were based on up to 122 914 participants from 25 studies. HRs are presented per 4·56 kg/m2 higher BMI, 12·6 cm higher waist circumference, and 0·083 higher waist-to-hip ratio (ie, 1 SD higher baseline values). Study-specific HRs were adjusted for age at baseline and smoking status, and stratified, where appropriate, by sex. Analyses were restricted to participants with BMI of 20 kg/m2 or higher. X-axes are shown on a log scale. p values for interaction were calculated by use of continuous values of variables, when appropriate. HRs for coronary heart disease, initially adjusted for age, sex, and smoking status, and then additionally adjusted for BMI, were 1·31 (1·24–1·37) and 1·23 (1·15–1·32), respectively, with waist circumference, and 1·29 (1·23–1·35) and 1·21 (1·16–1·26), respectively, with waist-to-hip ratio. HRs for ischaemic stroke, initially adjusted for age, sex, and smoking status, and then additionally adjusted for BMI, were 1·26 (1·19–1·33) and 1·26 (1·16–1·36), respectively, with waist circumference, and 1·25 (1·19–1·32) and 1·18 (1·13–1·24), respectively, with waist-to-hip ratio. BMI=body-mass index. HR=hazard ratio.
