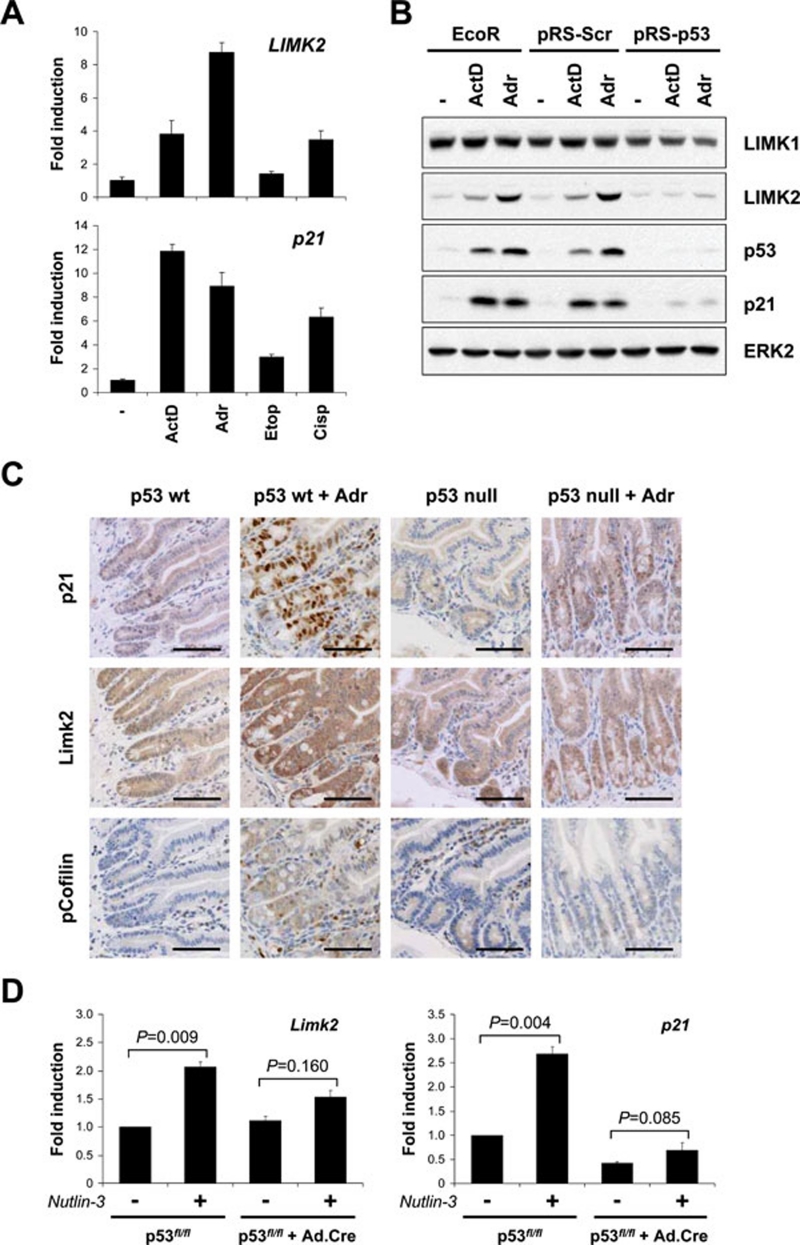
Figure 3.
LIMK2 induction by DNA damage is p53 dependent. (A) Genotoxic stress induces LIMK2 expression. MCF-7 cells were treated with ActD (2 nM), Adr (0.2 μg/ml), etoposide (Etop; 20 μM) or cisplatin (Cisp; 25 μM) for 24 h. LIMK2 and p21 mRNA levels were determined by qPCR. Data are presented as mean fold induction ± SEM (n = 3) relative to vehicle control. (B) p53 knockdown inhibits genotoxic stress-induced LIMK2 protein expression. Parental MCF-7-Eco, control MCF-7-pRS-Scr and p53-knockdown MCF-7-pRS-p53 cells were treated with ActD (2 nM) or Adr (0.2 μg/ml) for 24 h. Whole cell lysates were immunoblotted with antibodies against LIMK1, LIMK2, p53 or p21. Equivalent protein loading was confirmed by ERK2 immunoblotting. (C) Limk2 induction in mouse small intestinal crypts is p53-dependent. Immunohistochemical analysis of formalin-fixed/paraffin-embedded wild-type or p53-null small intestinal sections taken from mice treated with Adr (single i.p. dose of 10 mg/kg body weight) or saline vehicle control. Scale bars = 100 μm. (D) Nutlin-3 induction of Limk2 is dependent on p53. Following infection of p53fl/fl MEFs with or without Cre-recombinase-expressing adenovirus to delete p53, cells were treated with Nutlin-3 (50 μM) for 24 h. Limk2 and p21 mRNA levels were determined by qPCR. Data are presented as mean fold induction ± SEM in three separate p53fl/fl MEF lines. A two-tailed, paired Student's t-test was used to determine statistical significance.