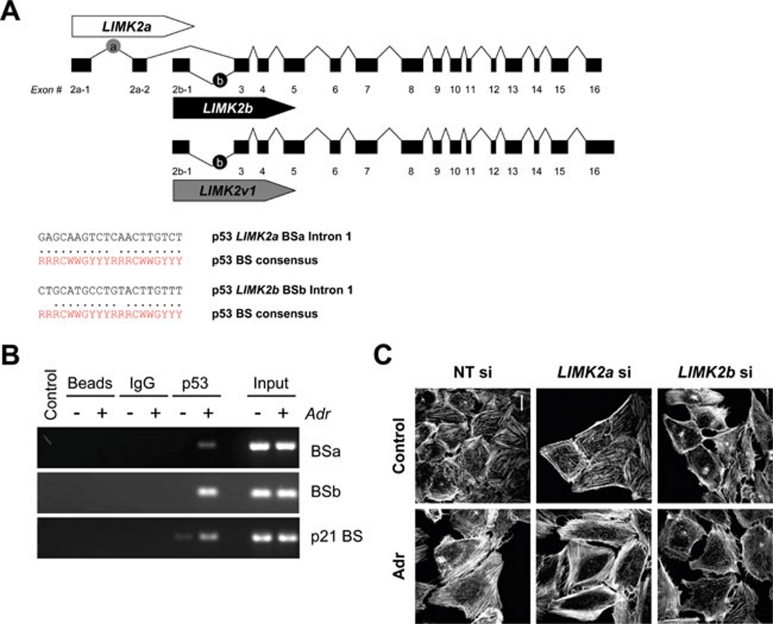
Figure 5.
LIMK2 is a direct p53 target gene. (A) Schematic diagram showing the exon-intron organization of human LIMK2 transcript variants. Potential p53-binding sites (BS) were identified by p53MH within the first intron (BSa) and the alternate first intron (BSb) of human LIMK2a and LIMK2b, respectively. Within each binding site, the individual half-sites are compared with the consensus p53-binding site sequence, where R = purine, Y = pyrimidine and W = adenine or thymine. (B) p53 binds to elements within intron 1 of LIMK2a and LIMK2b. Chromatin immunoprecipitation was performed with anti-p53 antibody (DO-7) on chromatin isolated from MCF-7 cells treated with and without Adr (adriamycin; 0.2 μg/ml) for 8 h. Ethidium bromide-stained agarose gels show PCR products of LIMK2 BSa and BSb after immunoprecipitation. Control immunoprecipitations were carried out with beads alone (Beads) or with control mouse IgG (IgG). Input represents 0.5% of the total chromatin used in each condition. (C) Knockdown of LIMK2b prevents Adr-induced stress fiber formation in U2OS cells. MCF-7 cells transfected with LIMK2b, LIMK2a or non-targeting (NT) control siRNAs were treated with Adr (0.2 μg/ml) for 24 h. Cells were then fixed and F-actin structures visualized with Texas Red-conjugated phalloidin. Scale bars = 20 μm.