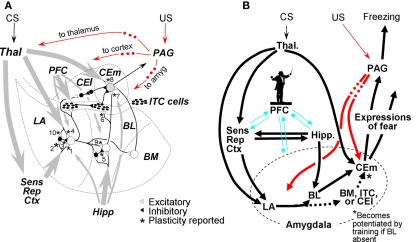
Figure 2.
Organization of amygdala fear-learning circuitry. (A) Major inputs to amygdala are gray arrows (thicker lines ∼ richer projections). US pathways are indicated in red; dots indicate that PAG projections to indicated targets are at least in part indirect. Synapses known to be plastic are starred and numbered for reference. Based on a figure from Pare et al. (2003). (B) Organization of FRAT fear-learning circuitry. Dotted BM/ITC/CEl pathway to CEm neurons becomes enabled by training if BL is lesioned. The silhouette of the conductor is intended to characterize our view of the role of PFC in fear-learning processes: We suggest that it plays an “executive” role in complex information processing tasks such as establishing new configural representations and consolidation as well as acting as a modulator of fear learning, expression, and extinction without actually mediating these processes or being the final repository of contextual representations or fear or inhibitory engrams (cf. Rudy et al., 2005). References for (A): 1. – Chapman et al. (1990), Huang and Kandel (1998); 2. – Mahanty and Sah (1998), Bauer and LeDoux (2004); 3. – Bauer and LeDoux (2004); 4. – Rogan and LeDoux (1995), Bauer et al. (2002); 5. – Marsicano et al. (2002); 6. – Royer and Pare (2002), Amano et al. (2010); 7. – Amano et al. (2010); 8. – Pare et al. (2004); 9. – Marsicano et al. (2002); 10. – Bauer and LeDoux (2004).