Figure 3.
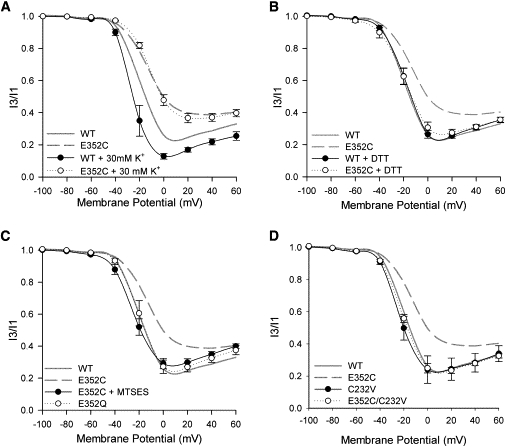
U-type inactivation can be restored to the E352C mutant by removing disulfide bonds. Each panel shows the inactivation-voltage relationship of wt and E352C channels under different test conditions. Unless otherwise stated, recordings were performed in ND96. Data are shown as mean ± SE, connected by simple spline curves; n > 3 for each data set. The inactivation-voltage relationships of wt and E352C channels under control conditions in ND96 are also shown for comparison (shaded and dashed spline curves, respectively). (A) Inactivation of the E352C mutant is not enhanced by 30 mM [K+]o. (B) Thirty-minute DTT pretreatment restores U-type inactivation to E352C channels. (C) Thirty-minute MTSES pretreatment restores U-type inactivation in E352C channels. Note that before treatment with MTSES, the oocyte was exposed to DTT for 30 min. U-type inactivation is unaffected by the E352Q mutation. (D) U-type inactivation is restored in the E352C/C232V double mutant. The inactivation-voltage relationship of the C232V mutation alone is not different from that of wt Kv2.1.
