Figure 2.
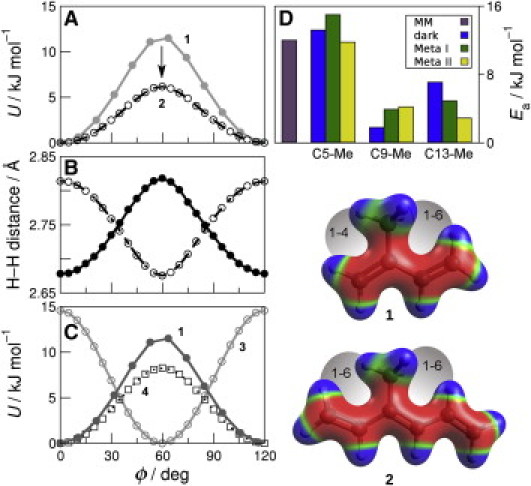
Torsional potential energy surfaces show that 1-6 interactions affect retinal methyl rotation. (A) Comparison of QM (circles) and MM (lines) methyl torsion angle energies in 1 and 2. (B) 1–6 distance in 2 between methyl hydrogen and C1 vinyl hydrogen (solid) and C5 vinyl hydrogen (open). (C) QM energy as a function of methyl torsion angle in 1, 3, and 4. (D) Activation energies (Ea) for C5-, C9-, and C13-Me groups from 2H NMR data for the dark, Meta I, and Meta II states of rhodopsin compared to a typical methyl dihedral energy barrier in a molecular mechanics force field. Steric interactions and electrostatic potentials are shown mapped to surfaces of 1 and 2.
