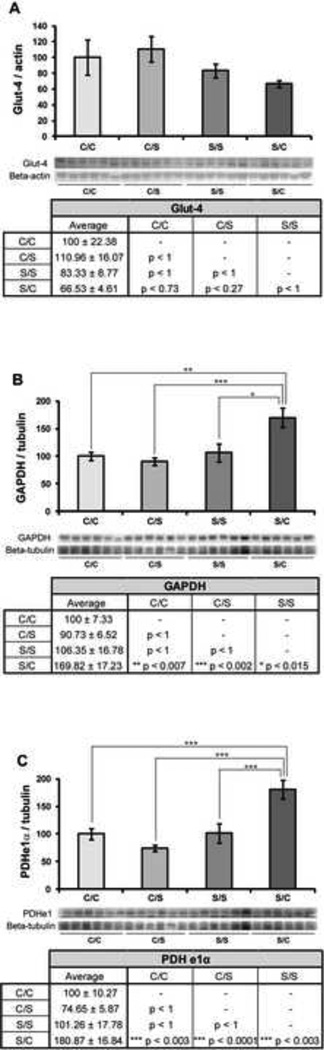
Figure 2. Effect of diet on glucose uptake and glycolysis.
Western blot analysis of Glut-4 (A), GAPDH (B), and PDHe1α (C) expression was performed on NHP hippocampal samples from each of the four diet paradigms. Expression levels for each sample were normalized to beta-actin levels (Glut-4) and beta-tubulin levels (GAPDH and PDHe1α). Expression levels were then normalized to the C/C diet (C/C was set to 100%). Statistically significant differences were calculated using a two-tailed, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by a Bonferroni post-hoc correction. Diet paradigm significantly affected GAPDH and PDHe1α expression in the NHP hippocampus. Bars represent % C/C ± S.E.M., n = 6 for each condition, p<0.05*, p<0.01**, p<0.005***.