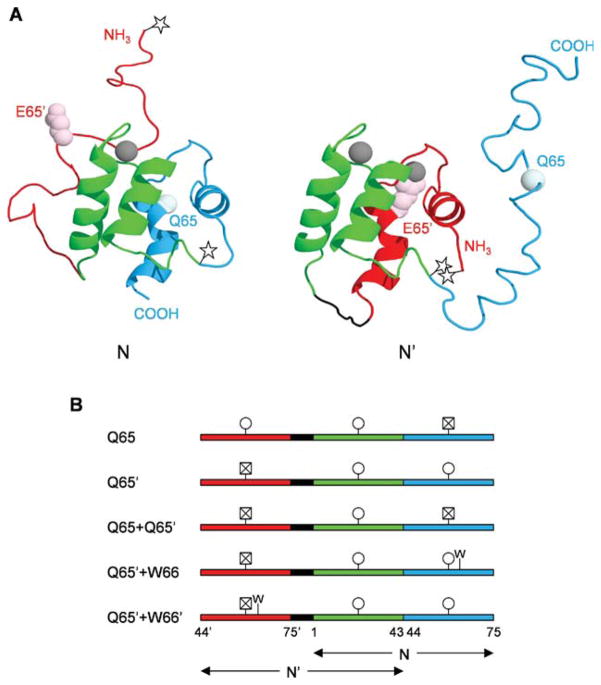
Figure 1.
Structures and amino acid sequences of calbindin-AFF variants. (A) Predicted structures of N and N′ conformations. The color scheme is as follows: red, hand-2′ (residues 44′–75′); green, hand-1 (residues 1–43); blue, hand-2 (residues 44–75). The side chain of E65′ is shown in light pink and the alpha carbon of Q65 is shown in pale cyan. Calcium ions are depicted as gray spheres. The Q65 variant is shown in which calcium binding induces the red region to fold and the blue region to unfold. The stars mark the location of Cys residues to which fluorophores are attached, to track the N–N′ conformational change. (B) Amino acid sequences of calbindin-AFF variants showing the shared sequence in green and the duplicated sequences in red and blue, as in Panel A. The black segment is a six-amino acid linker. Circles indicate viable calcium binding sites; crossed-out squares denote calcium binding sites made nonfunctional by the presence of the Q65 or Q65′ mutation. The presence of the F66W mutation is marked by W.