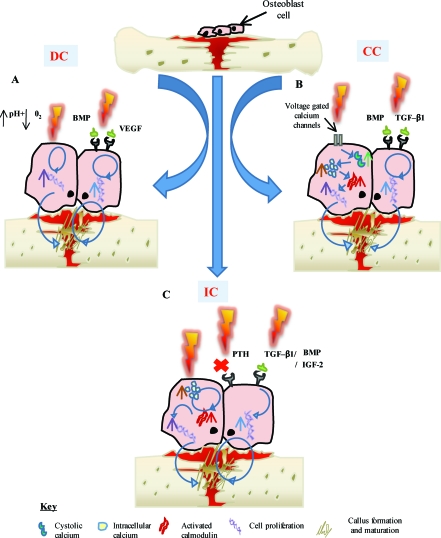
Figure 3.
The proposed mechanism of action of the different types of electrical stimulation methods. (a) Proposed mechanism for direct current (DC). Direct current lowers the oxygen level and increases the pH, which causes an increase in osteoblast cell proliferation. This in turn enhances callus formation and maturation, leading to bone healing. All 3 types of ES enhance growth factors. This in turn increase cell proliferation, which enhances callus formation and maturation, leading to bone healing and improved clinical outcome. (b) Proposed mechanism for capacitive coupling (CC). Capacitive coupling causes an increase in cystolic calcium through voltage gated calcium channels. This then increases intracellular calcium, which in turn enhances activated calmodulin stores. Cell proliferation then increases, which enhances callus formation and maturation, leading to bone healing. (c) Proposed mechanism for inductive coupling (IC). Inductive coupling causes a direct increase in intracellular calcium, which in turn enhances activated calmodulin stores. Cell proliferation is increased, which enhances callus formation and maturation, leading to bone healing. BMP indicates bone morphogenetic protein; IGF-2, insulin growth factor 2; PTH, parathyroid hormone; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor beta 1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.