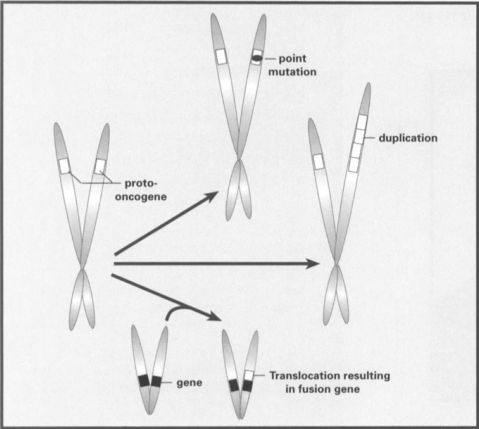
Figure 1.
Typical mutations transforming a normal proto-oncogene into an oncogene. The most common types of mutations associated with oncogenes involve point mutations that alter the control of the oncoprotein made from the gene (as in the ras family of oncogenes), duplication of oncogenes resulting in higher expression of the oncogene, or chromosomal translocations that fuse the oncogene with a different gene. The latter change either results in an oncoprotein of altered function or results in changes in expression pattern of the oncogene