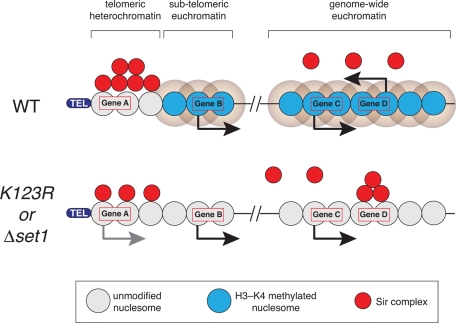
FIGURE 6:
Model for ectopic silencing of euchromatic genes in the absence of H2B–H3 cross-talk. In WT cells, H3K4 methylation at subtelomeric and genome-wide euchromatin keeps Sir proteins localized to telomeric heterochromatin and prevents them from associating from transcribed genes. In the absence of H3K4 methylation (as occurs in htbK123R and Δset1 cells), Sir proteins dissociate from the telomeres, leading to activation of subtelomeric genes (e.g., gene A) and their ectopic association with select euchromatic genes (e.g., gene D), silencing their expression. In this model, gene D would correspond to a category 4 gene.