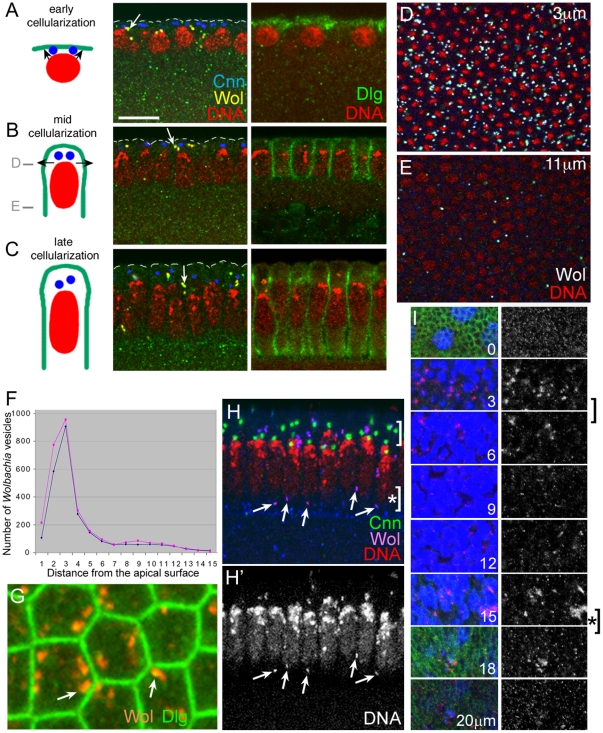
Figure 2. Wolbachia vesicles are enriched near new membrane addition sites.
For detecting Wolbachia, anti-Dlg antisera was used for A, B, and C, anti-Vang antisera were used for H and I, while both anti-Vang and anti-Dlg antisera were used for G, and both anti-Vang and anti-Sdt antisera were used for D and E. DNA was visualized with propidium iodide in all images except G and I. (A,B,C) Left, At the onset of cellularization, new membrane addition occurs at the apical region (arrows in A). At mid-cellularization stage, major membrane addition site is sub-apical region (arrows in B). At the end of cellularization, elongated nuclei are separated by newly formed cell boundary (C). The blue dots represent centromes, the red ovals are nuclei, and the green lines are membranes. This diagram is based on information from Lecuit and Wieschaus [27]. Middle, Wolbachia vesicles are indicated with arrows. Centrosomes visualized with Centrosomin antibody (blue) are present at the apical region. Right, Dlg (green) is present at the membrane. Nuclei are initially round and become elongated as the cellularization proceeds (red). (D–F) Among the 15 tangential sections with 1 µm interval, the Wolbachia vesicles are most enriched at 3 µm from the apical surface (D), and are almost absent at the basal level at mid-cellularization stage (E). The planes of confocal sections, D and E, are indicated in B with grey bars. Number of Wolbachia vesicles in these 15 tangential sections was counted with NIH Image J program (F). The number of Wolbachia vesicles was separately counted from the data obtained with two antisera that can recognize Wolbachia [13]. (G) Wolbachia vesicles are located close to the plasma membrane (arrows). (H) A cross-section of embryo cortex at the end of cellularization. Wolbachia vesicles are localized not only in the sub-apical region (bracket) but also in the basal region (arrows, bracket with asterisk). (I) Wolbachia vesicles are visualized by serial tangential sections of epithelial cells in a wing disc. Density of Wolbachia vesicles is highest around 2–6 µm from the apical surface (bracket), and a minor fraction of Wolbachia is present near the basal position (bracket with an asterisk). Dlg was visualized as a membrane marker (green). Wolbachia, stained with both DAPI (blue) and anti-Vang antibody (red), appear as pink. Scale bar: A–C, 10 µm; D,E,H,I, 14 µm; G, 3.7 µm.