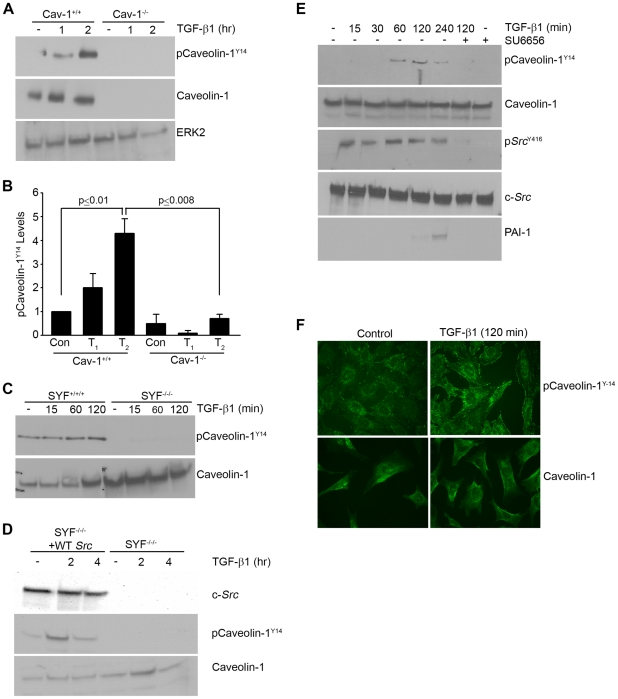
Figure 6. c-Src is an upstream regulator of caveolin-1Y14 phosphorylation.
MEFs were serum-deprived for 1 day prior to incubation with TGF-β1 (0.1 ng/ml) for the times indicated. Western analysis indicated that TGF-β1 stimulated caveolin-1 phosphorylation at the Y14 c-Src kinase target site in caveolin-1+/+ fibroblasts but not, as expected, in caveolin-1−/− cells (A,B). CaveolinY14 phosphorylation is similarly evident extracts of SYF+/+/+ but not in SYF−/−/− MEFs (C). Stable expression of a pp60c-src construct (+WT Src) in SYF−/−/− fibroblasts is sufficient to rescue caveolinY14 phosphorylation in response to TGF-β1 (but not in empty vector expressing SYF−/−/− cells) despite comparable caveolin-1 expression in both cell types (D). Pretreatment of serum-deprived VSMC with the Src kinase inhibitor SU6656 (2 µM) prior to addition of TGF-β1 (1 ng/ml) eliminated TGF-β1-induced Src Y416 activation, caveolinY14 phosphorylation and PAI-1 expression (E). Total ERK2 (A,B), caveolin-1 (C,D,E) and c-Src (E) were approximately constant under all culture conditions providing internal loading controls. Data plotted in (B) represent the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. To assess potential growth factor-associated changes in caveolin-1 localization, subconfluent serum-deprived MEFs were stimulated with TGF-β1 (0.1 ng/ml) for 2 hrs and the distribution of phospho-caveolin-1Y14 and total caveolin-1 assessed by immunocytochemistry; control cells remained untreated (F).