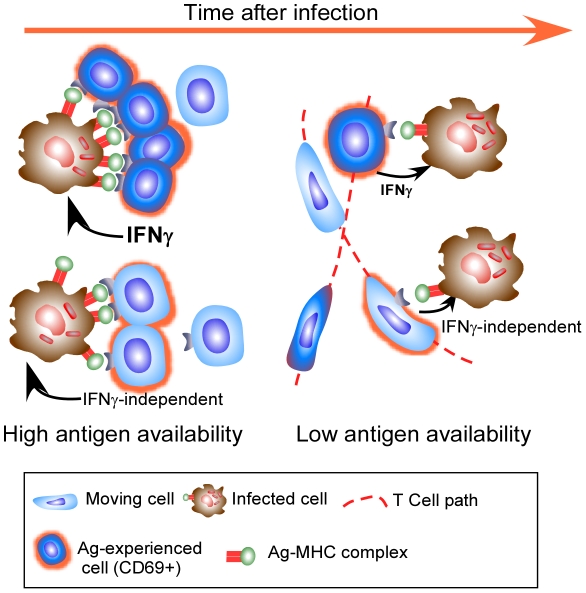
Figure 1. Effector T cells do not find the granuloma to be a stimulating environment.
Effector T cells enter the granuloma and only a few exhibit significant migration arrest (dark blue cells) and targeted release of IFNγ, likely when they encounter a high level of cognate antigen on infected phagocytes. As their cognate antigen is reduced, even fewer cells undergo migration arrest, with many more cells continuing to move throughout the granuloma (light blue motile cells). Although these cells do not stop migrating, they do up regulate CD69 in an antigen-specific manner. Cells entering the granuloma may mediate their effector function without the release of IFNγ, and while this activity does require recognition of antigen, it may not need migration arrest.