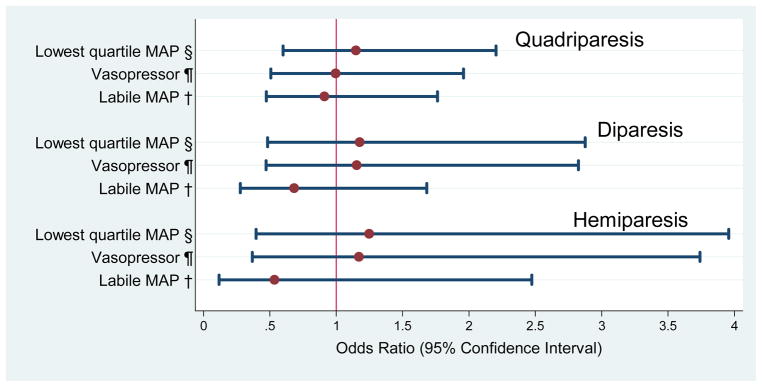
Figure 3.
Odds ratios (and 95% confidence intervals) of the risk of cerebral palsy types obtained with logistic regression models that incorporate indicators of hypotension during the first 24 postnatal hours and potential confounders.*
*Adjustment is made for black race, public insurance, primagravida, male sex, gestational age 23–24 weeks, birth weight Z-score < -1, multi-fetal gestation, delivery for preeclampsia or fetal indication and receipt of magnesium. A hospital strata term is included to account for the possibility that infants born at a particular hospital are more like each other than like infants born at other hospitals.
§Low Q: lowest MAP recorded in the first 24 hours in the lowest quartile for gestational age
¶Vaso: treatment for hypotension with a vasopressor in the first 24 hours with any vasopressor (dopamine, dobutamine, and epinephrine)
†Labile: labile blood pressure, defined as the upper quartile of the difference in the lowest and highest MAP