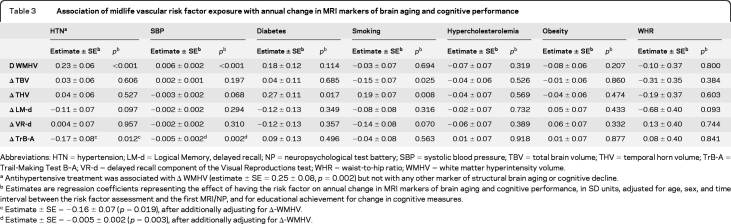
Table 3.
Association of midlife vascular risk factor exposure with annual change in MRI markers of brain aging and cognitive performance
Abbreviations: HTN=hypertension; LM-d=Logical Memory, delayed recall; NP=neuropsychological test battery; SBP=systolic blood pressure; TBV=total brain volume; THV=temporal horn volume; TrB-A=Trail-Making Test B–A; VR-d=delayed recall component of the Visual Reproductions test; WHR=waist-to-hip ratio; WMHV=white matter hyperintensity volume.
Antihypertensive treatment was associated with Δ WMHV (estimate ± SE = 0.25 ± 0.08, p = 0.002) but not with any other marker of structural brain aging or cognitive decline.
Estimates are regression coefficients representing the effect of having the risk factor on annual change in MRI markers of brain aging and cognitive performance, in SD units, adjusted for age, sex, and time interval between the risk factor assessment and the first MRI/NP, and for educational achievement for change in cognitive measures.
Estimate ± SE = −0.16 ± 0.07 (p = 0.019), after additionally adjusting for Δ-WMHV.
Estimate ± SE = −0.005 ± 0.002 (p = 0.003), after additionally adjusting for Δ-WMHV.