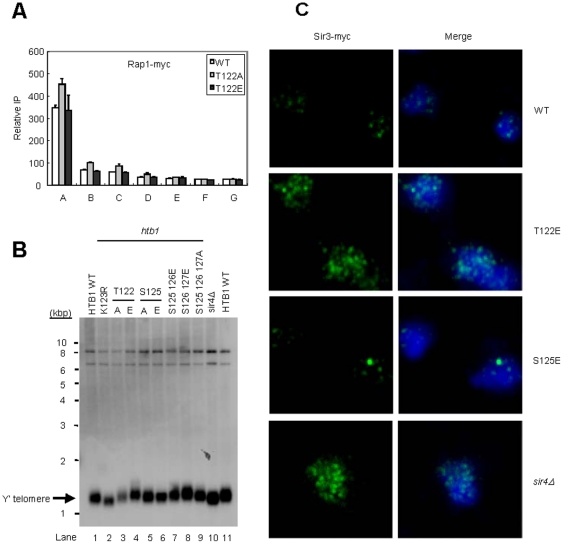
Figure 5. htb1-T122E disrupts telomere clustering.
(A) Rap1 distribution on the end of Chr. VI-R in the strains derived from Y131 with Rap1-myc expressing HTB1 WT, htb1-T122A and htb1-T122E was analyzed by chromatin immunoprecipitation and then detected by quantitative PCR. (B) Telomere length determination in the indicated strains derived from UCC6389. Genomic DNA were extracted, digested with XhoI, and analyzed by Southern blot using probes specific to Y′-telomere DNAs. (C) Indirect immunofluorescence of telomere ends in yeast strains derived from Y131 expressing HTB1 WT, htb1-T122E, or htb-S125E, or with sir4Δ. All strains carry a myc-tagged SIR3 allele in the genome for monitoring telomere foci. Cells fixed and permeabilized on glass slides were decorated with mouse α-myc monoclonal antibodies (for Sir3) and antibody complexes were later bound with Alexa Fluor 488 goat α-mouse IgG antibodies for visualization. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Sir3 is in the green channel (left); DAPI is in the blue channel (right).