Fig. 7.
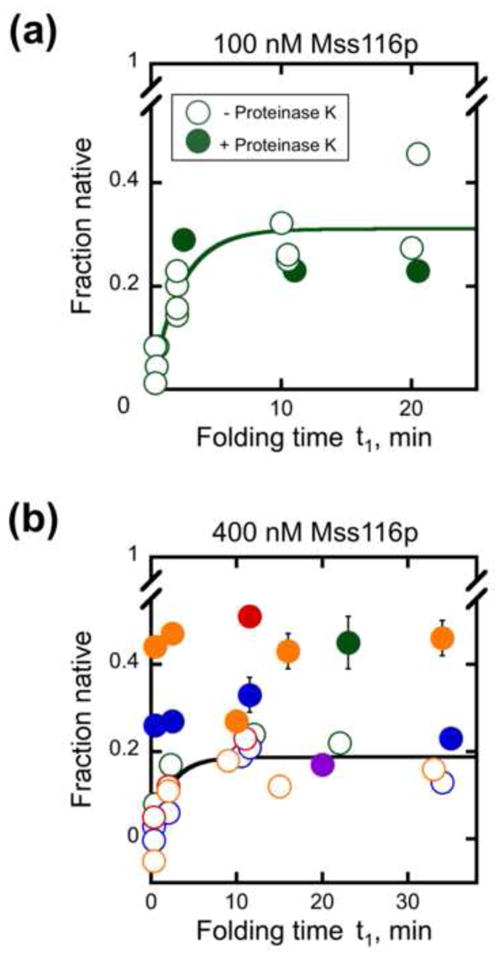
Proteolysis of Mss116p after incubation with D135 RNA in the absence of ATP. Mss116p was added in stage 1 at 100 nM (panel a) or 400 nM (panel b) and incubated for the indicated times under near-physiological conditions. Proteinase K (1 mg/ml) was then added at the indicated times (closed symbols) and incubated for an additional 8 – 60 min to permit further folding before aliquots were transferred to stage 2 and the fraction of native ribozyme was determined by measuring the substrate cleavage burst amplitude. The fraction of native ribozyme did not depend on the incubation time after proteinase K addition (8–60 min), and the symbols show the average values. Open symbols show equivalent reactions with Mss116p and without nucleotide, to which proteinase K was not added. Including or omitting 0.5% SDS with proteinase K to ensure removal of peptide fragments had no significant effect on the results (data not shown). For the experiments shown in panel b, 0.5% SDS was added immediately after proteinase K. Results from independent determinations are shown in different colors. It can be seen that the increase in native ribozyme upon proteinase K treatment is variable and that the variation is larger between experiments than within experiments.
