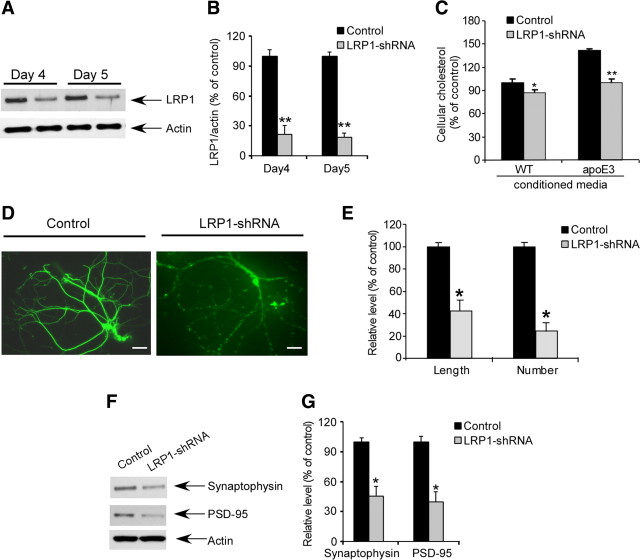
Figure 6.
LRP1 knockdown in primary neurons results in neurite degeneration. A, Primary cortical neurons cultured from wild-type C57BL/6J mice were infected by lentivirus carrying LRP1-shRNA on day 8 of in vitro culture. On day 4 and day 5 after infection, LRP1 expression was analyzed by Western blotting. B, Densitometric quantification of LRP1 expression showed that LRP1 was effectively knocked down on day 5 after infection with lentiviral shRNA. C, Following infection of lentiviral LRP1-shRNA in primary neurons, conditioned media from astrocytes of wild-type (WT) control or apoE3 target replacement mice with equal amounts of apoE were added and incubated with neurons for 24 h. Total cholesterol content in neurons under each condition was measured. D, Following infection of lentiviral LRP1-shRNA in primary neurons, conditional media from WT astrocytes was added to the neuronal culture media and immunofluorescence staining was assessed using a microtubule-associated protein (MAP)-2 antibody (detected by Alexa 488, green). Shown are images of representative staining. E, Quantification of neurite length and numbers of MAP-2 staining neurons indicates that LRP1 knockdown significantly reduces the length and numbers of neurites in primary cultured neurons. F, Following infection of lentiviral LRP1-shRNA in primary neurons, expression of synaptophysin, PSD-95, and actin was analyzed by Western blotting. G, Densitometric quantification of Western blots in F showed that the expression of synaptophysin and PSD-95 was significantly decreased in LRP1 knocked down neurons. The data represent the means ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.