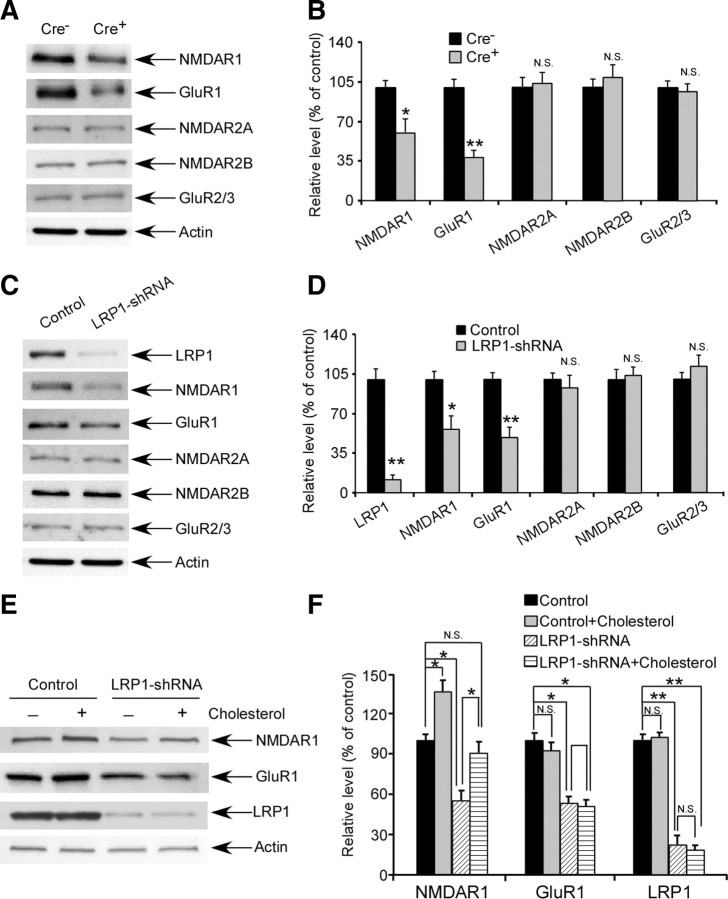
Figure 7.
LRP1 deletion leads to decreased levels of NMDAR1 and GluR1. A, Expression of NMDAR1, NR2A, NR2B, GluR1, and GluR2/3 in the cortex were evaluated in 18-month-old Cre+ and Cre− mice by Western blotting. B, Densitometric quantification of Western blots in A was performed as described in Experimental Procedures (n = 4). Note that expression of NMDAR1 and GluR1 was significantly reduced in Cre+ mice. C, Primary cortical neurons cultured from wild-type C57BL/6J mice were infected by lentivirus carrying LRP1-shRNA on day 8 of in vitro culture. On day 5 after infection, expression of LRP1, actin, NMDAR1, NR2A, NR2B, GluR1, and GluR2/3 were analyzed by Western blotting. D, Densitometric quantification of Western blots in C showed that expression of NMDAR1 and GluR1 was significantly reduced in LRP1 knocked down neurons. E, Following infection of lentiviral LRP1-shRNA or control lentivirus in primary neurons, cholesterol was added to the neuronal culture media for 2 d and Western blotting was performed to assess the expression of LRP1, NMDAR1, and GluR1. F, Densitometric quantification of expression of LRP1, NMDAR1, and GluR1 showed that expression of NMDAR1, but not GluR1, was partially rescued by cholesterol in LRP1 knocked down neurons. The data represent the means ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.