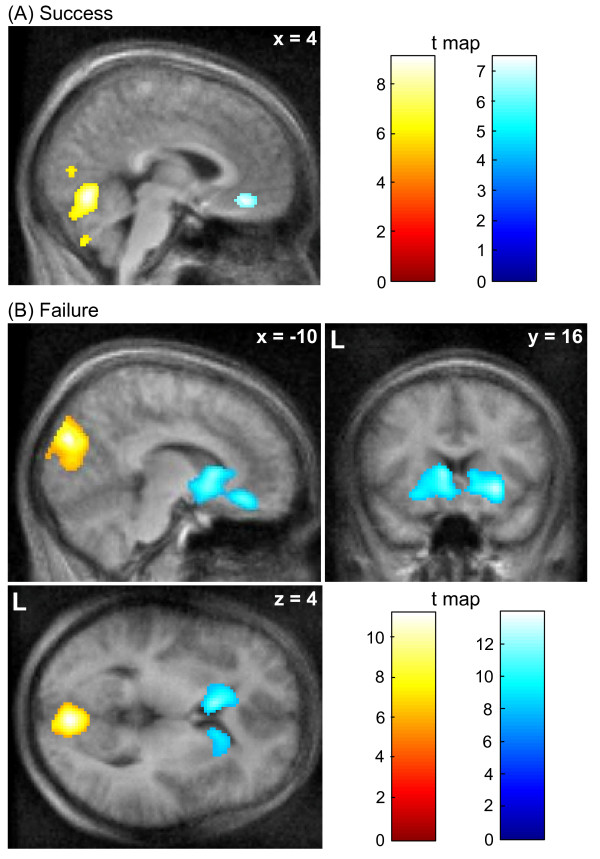
Figure 1.
Statistical maps on activation and deactivation during success (A) and failure events as compared to baseline (B; FWE corrected p < 0.05). Both success and failure were associated with increased visual or cerebellar activity. Success led to deactivation of the rACC. The caudate nucleus and orbitofrontal cortex showed deactivation in response to failure.