Fig. 4.
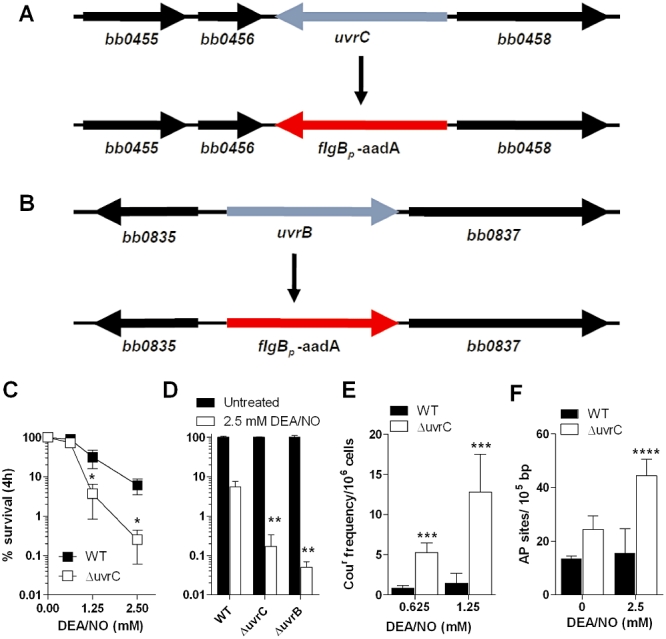
RNS-dependent damage to B. burgdorferi DNA is repaired by the nucleotide excision repair pathway.
A. A diagram is shown for the deletion of uvrC (bb0457) with a flgBp::aadA resistance cassette. The NER gene uvrC (blue) was replaced by allelic exchange using a suicide vector harbouring a streptomycin resistance cassette under the control of a flgB promoter (red) flanked by the 1 kb upstream and downstream regions (black) of uvrC as described in Experimental procedures.
B. A diagram is shown of the deletion strategy for uvrB (bb0836) and replacement with a flgBp::aadA resistance cassette using the strategy outlined in (A).
C. B31 A3 (WT) and B31 A3 Δuvrc::aadA (ΔuvrC) cells were treated with 0 mM, 0.625 mM, 1.25 mM and 2.5 mM DEA/NO under microaerobic conditions for 4 h. The % survival was determined by enumerating cfu following plating on P-BSK. *P < 0.005 compared with untreated controls.
D. B31 A3 (WT), B31 A3 ΔuvrC::aadA (ΔuvrC) and B31 A3 ΔuvrB::aadA (ΔuvrB) cells were treated with 0 mM or 2.5 mM DEA/NO under microaerobic conditions for 4 h. Per cent survival was determined by enumerating cfu following plating on P-BSK. **P < 0.005 compared with wild-type controls.
E. The spontaneous resistance frequency to 250 ng ml−1 coumermycin A was determined for B31 A3 (WT) and B31 A3 Δuvrc::aadA (ΔuvrC) cells treated with 0.625 mM or 1.25 mM DEA/NO for 4 h. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. ***P < 0.005 compared with untreated controls.
F. The number of AP sites were measured in DNA harvested from wild-type and ΔuvrC::aadA B. burgdorferi challenged with 2.5 mM DEA/NO for 4 h. Data represent the mean ± SD of three biological samples. ****P < 0.001 compared with untreated controls.
