Fig. 4.
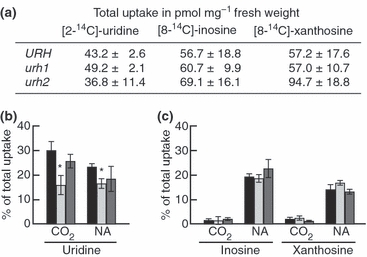
Nucleoside uptake and metabolism in wild-type and mutant plants. (a) Total uptake after feeding 14C-nucleosides to roots of Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Data show mean ± SD (n = 2–4). (b) 14CO2 formation and 14C incorporation into nucleic acids (NA) after feeding [2-14C]-uridine to roots of A. thaliana plants. Data show mean ± SD (n= 4). Significant differences (P < 0.05) between mutants (urh1, pale gray bars; urh2, dark gray bars) and wild-type (URH, black bars), as determined using unpaired two-tailed t-tests, are marked with an asterisk. (c) 14CO2 formation and 14C incorporation into nucleic acids (NA) after feeding [8-14C]-inosine and [8-14C]-xanthosine to roots of A. thaliana plants. Data show mean ± SD (n = 2–4). No significant differences (P < 0.05) between mutants (urh1, pale gray bars; urh2, dark gray bars) and wild-type (URH, black bars) were found. URH, nucleoside hydrolase.
