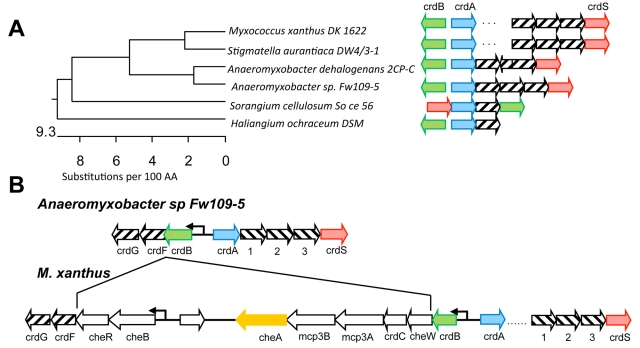
FIG 1 .
Addition of a chemosensory module in proximity to a prototypical TCS in Myxococcus xanthus. (A) A 16S rRNA gene phylogenetic tree of members of the Myxococcales order was generated using DNASTAR MegAlign. Arrows indicate the gene orientation of the crdS (red), crdA (blue), crdB (green), and cheA (orange) homologs. Homologs were identified by BLAST (41). Striped arrows indicate conserved homologs. The dots between crdA and crdS in M. xanthus and S. aurantiaca DW4/3-1 indicate an insertion. Only M. xanthus and S. aurantiaca DW4/3-1 contain homologs of the che3 system. Other organisms maintain crdSAB conservation but lack the che3 system. (B) Illustration of the crdSAB regions in Anaeromyxobacter sp. Fw109-5 and M. xanthus. Sequences present in M. xanthus and S. aurantiaca suggest the che3 cluster was obtained by insertion between the crdB and crdF homologs, relative to those shown for Anaeromyxobacter sp. Fw109-5. Anaeromyxobacter Fw109-5 is closely related to M. xanthus but lacks the che3 cluster. Numbered ORFs encode (1) a penicillin binding protein, (2) a FG-GAP protein, and (3) a protein containing an SBP_bac5 domain. White arrows represent the M. xanthus che3 cluster described previously (18).