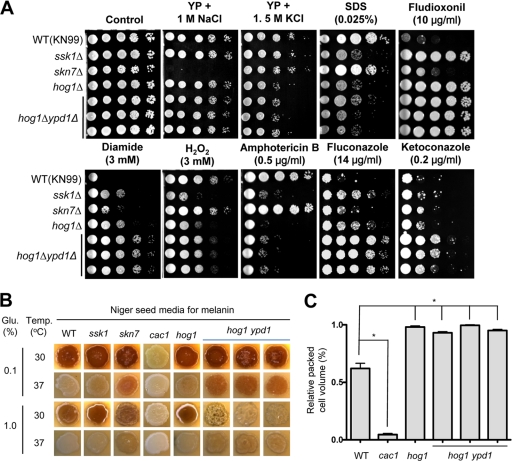
Fig. 2.
Comparative phenotypic analysis of the ypd1Δ hog1Δ mutant. (A) The role of Ypd1 in stress and antifungal drug responses. Each C. neoformans strain (MATa WT [KN99a] and ssk1Δ [YSB429], skn7Δ [YSB433], hog1Δ [YSB81], and ypd1Δ hog1Δ [YSB779, YSB780, and YSB781] mutant strains) was 10-fold serially diluted (1 to 104 dilutions) and spotted (4 μl of each dilution) on YP or YPD agar containing the indicated concentration of NaCl, KCl, SDS, diamide, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), fludioxonil, amphotericin B, fluconazole, or ketoconazole. Cells were incubated at 30°C for 2 to 3 days and then photographed. (B) The role of Ypd1 in melanin biosynthesis. For melanin production, each C. neoformans strain (MATa WT [KN99a] and ssk1Δ [YSB429], skn7Δ [YSB433], cac1Δ [YSB79], hog1Δ [YSB81], and ypd1Δ hog1Δ [YSB779, YSB780, and YSB781] mutant strains) was grown for 16 h in YPD medium, spotted on solid Niger seed medium containing either 0.1% or 1% glucose (Glu.), incubated at either 30°C or 37°C for 2 days, and then photographed. (C) The role of Ypd1 in capsule biosynthesis. Capsule synthesis levels for each C. neoformans strain were quantitatively measured by using hematocrit as described before (10). Error bars show standard deviations. *, P < 0.001.