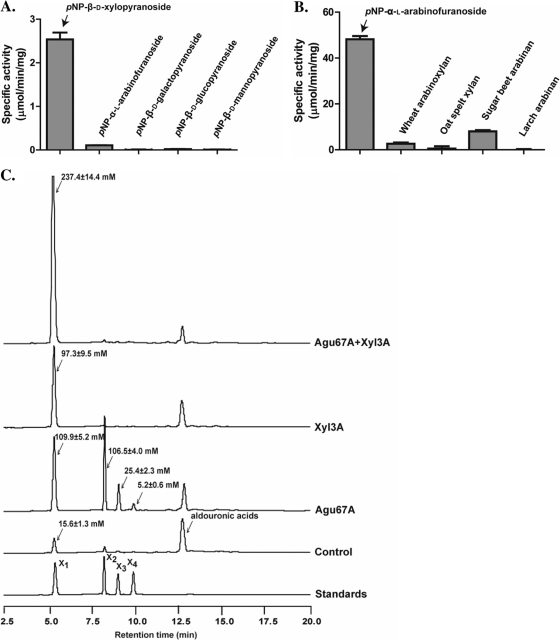
Fig. 3.
Functional analyses of the gene products of R. albus 8 xyl3A, ara51A, and agu67A. (A) Hydrolysis of pNP-linked sugars by R. albus 8 Xyl3A. The Xyl3A protein was incubated with different sugars linked to pNP, and the cleavage of the linkage was estimated as the amount of pNP released into the reaction mixture. (B) Hydrolysis of arabinose-containing substrates by R. albus 8 Ara51A. The catalytic activity of Ara51A was estimated by use of pNP-linked substrates and also with natural substrates (wheat arabinoxylan, oat spelt xylan, sugar beet arabinan, and larch arabinan). The catalytic activities on pNP-linked substrates were determined as described for panel A, and the activities on the natural substrates were determined by quantifying the amounts of reducing ends released during incubation with Ara51A. (C) Catalytic activity of Agu67A. The catalytic activity of the R. albus Agu67A was determined by its capacity to release xylo-oligosaccharides from aldouronic acids and also to function synergistically with a β-xylosidase (R. albus 8 Xyl3A) to release xylose from aldouronic acids. The hydrolytic products were analyzed by HPAEC with pulsed amperometric detection (HPAEC-PAD) and identified by comparison of peaks with retention times of xylo-oligosaccharides as standards.