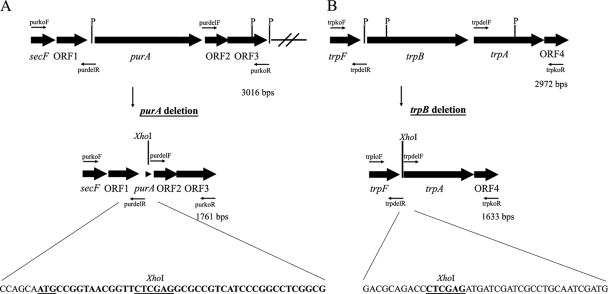
Fig. 1.
Sequential deletion of the R. marinus purA and trpB genes. (A) Gene organization flanking the R. marinus strain PRI 493 purA gene. The open reading frames secF, ORF1, and purA show homology to genes encoding a protein export membrane protein, an anti-sigma factor antagonist, and adenylosuccinate synthase, respectively. The products of ORF2 and ORF3 show homology to conserved hypothetical proteins. PstI restriction sites (P) are indicated. The purkoF and purkoR primers were used to amplify the sequence, while the purdelR and purdelF primers were used to replace bases 16 to 1276 from the purA ORF with an XhoI restriction site. The remaining purA sequence (38 bp) in the deletion plasmid pKO4 as well as in the genome of strain SB-32 is shown (in bold type with the start codon underlined) as well as six bases of the 5′ flanking sequence. (B) Gene organization surrounding the R. marinus PRI 493 trpB gene. The trpB and trpA genes encode tryptophan synthase components B and A, respectively. They are flanked by a gene showing homology to trpF and encoding phosphoribosylanthranilate isomerase and a gene encoding a hypothetical protein (ORF4). PstI recognition sites (P) are indicated. The region was amplified using primers trpkoF and trpkoR, and the entire trpB ORF and the trpBA intergenic sequence were replaced with a unique XhoI site. The sequences that flank the XhoI site in the trpB deletion plasmid pKO9 and also in the genome of SB-62 are shown.