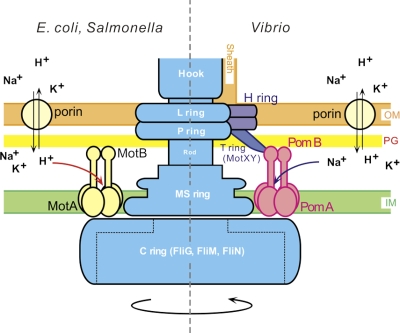
Fig. 1.
A schematic diagram of two types of flagellar motors. A hypothetical model for the proton-driven motor of E. coli or Salmonella (left) and the sodium-driven motor of Vibrio (right). The sodium-driven polar flagellum of Vibrio is sheathed. The energy source for flagellar motor rotation is provided by an electrochemical potential gradient across the inner membrane. The functional units of the stator are thought to be (MotA)4(MotB)2 and (PomA)4(PomB)2 (3, 26, 49). IM, inner membrane; PG, peptidoglycan layer; OM, outer membrane.