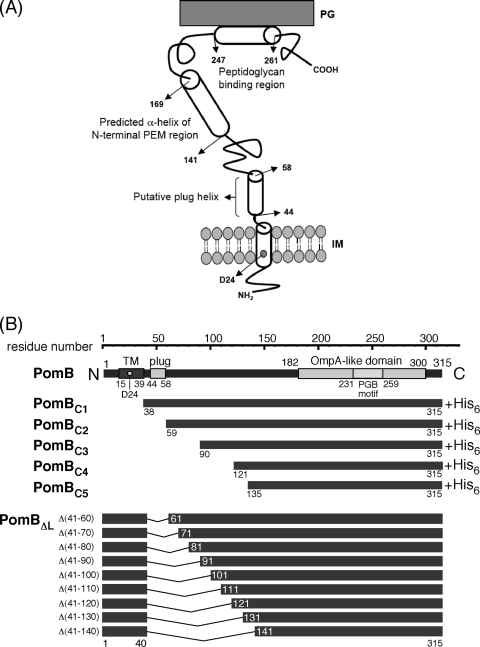
Fig. 1.
The PomB topology model and constructs used in this study. (A) The putative topology of PomB. PomB contains 315 amino acids and has a single TM segment (residues 15 to 39) and a plug segment (residues 44 to 58, speculated to prevent premature Na+ translocation across the cell membrane) at its N terminus. D24 is regarded as the critical Na+ binding site. Amino acids 143 to 169 are predicted to form a putative N-terminal helix of the PEM region. The large periplasmic region includes an OmpA-like domain (residues 182 to 300) with a PGB motif (residues 231 to 259). The putative helix (residues 247 to 261) that may form the dimer interface in the PGB domain is also indicated. (B) Primary structure of PomB and schematic representation of N-terminally-truncated PomB fragments (PomBC) and in-frame deletions (PomBΔL). The in-frame-deletion derivatives constructed in this study lack the putative plug segment and part of the periplasmic linker region. IM, inner membrane.