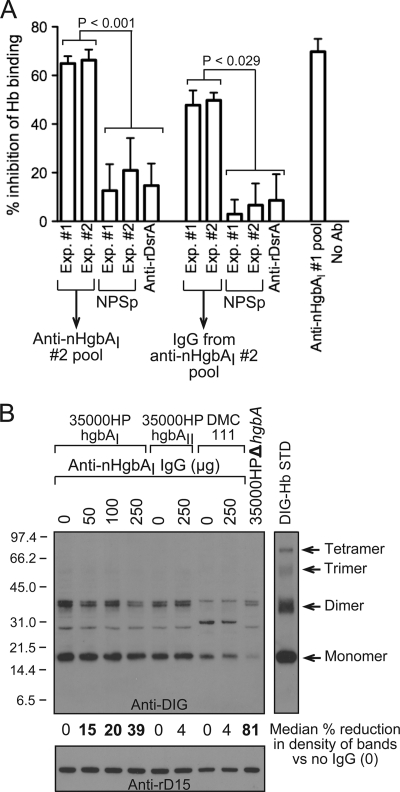
Fig. 6.
Anti-nHgbAI Abs partially block Hb binding by HgbA. (A) The abilities of pooled nHgbAI antisera or purified IgG to block binding of DIG-Hb to nHgbAI were measured using an Hb blocking ELISA. The anti-nHgbAI 1 pool from a previous study was used as a positive control (1), while the irrelevant polyclonal antisera to the outer membrane trimeric autotransporter DsrA (anti-rDsrA) was used as a negative control (48). Results are expressed as the percentage of a no-antibody control, arbitrarily defined as 0% inhibition of DIG-Hb binding to nHgbA. Data were compared using a Mann-Whitney rank sum test. NPSp, normal pig serum pool. (B) The abilities of anti-nHgbAI 2 IgG to block binding of DIG-Hb to H. ducreyi strains 35000HPhgbAI, 35000HPhgbAII, and DMC111 were analyzed using a whole-cell Hb blocking assay. Bands on the Western blot were analyzed with NIH Image (version 1.62) and are arbitrarily expressed as the percent reduction in band density compared to the strain plus DIG-Hb without the addition of IgG (indicated as 0). Bold numbers indicate a statistically significant reduction in band density (Mann-Whitney rank sum test). The DIG-Hb lane (10 ng) served as a standard (STD). Shown is a representative Western blot from 4 different experiments with similar results.