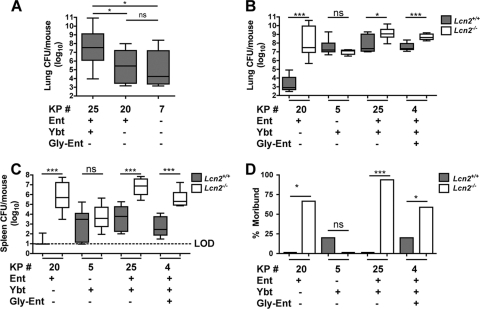
Fig. 3.
Yersiniabactin is sufficient to evade Lcn2 and cause pneumonia but not sepsis. (A) Lung bacterial burden (log10 CFU) at day 3 after retropharyngeal inoculation of 1 × 104 CFU of the K. pneumoniae mutants indicated (KP #) was determined in C57BL/6 mice (n ≥ 10 mice per group). Box-and-whisker graph shows the median and interquartile ranges. *, P < 0.05 as determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post test. ns, not significant. (B, C) Lung (B) and spleen (C) bacterial burdens at day 3 after retropharyngeal inoculation of 1 × 104 CFU of the K. pneumoniae mutants indicated were compared between C57BL/6 (Lcn2+/+) and isogenic Lcn2−/− mice (≥5 mice per group). *, P < 0.05, and ***, P < 0.001, as determined by the Mann-Whitney test. Box-and-whisker graphs show the median and interquartile ranges. LOD, limit of detection. (D) The percentages of dead or moribund mice were determined at day 3 after inoculation. *, P < 0.05, and ***, P < 0.001, as determined by the log rank test. The siderophore genotype of each strain is indicated by plus signs (+). ns, not significant.