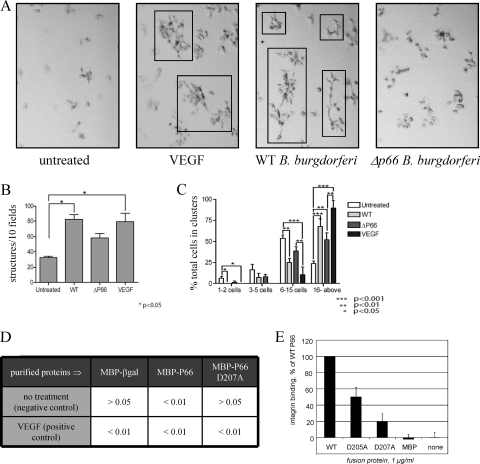
Fig. 3.
B. burgdorferi promotes growth and structure formation by endothelial cells in Matrigel. Cells were plated at low density on either conventional plastic tissue culture plates or on the same culture plates precoated with Matrigel. After 2 days of incubation, the cells were treated with recombinant vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), B. burgdorferi, or the medium control and followed visually over several days of additional incubation. (A) Representative micrographs from day 5 postinfection or posttreatment. Multicellular structures distinct from clumps are boxed. Wild-type (WT) B. burgdorferi and Δp66 B. burgdorferi were examined. (B) Quantification of multicellular structures on day 5. At earlier time points, there were no statistically significant differences between the values for the different conditions. On day 5, the number of structures in the cells infected with WT B. burgdorferi or in the cells treated with VEGF was significantly higher (P < 0.05) than that of the untreated cells. (C) Quantification of overall endothelial cell growth to form multicellular clusters and structures. The growth and formation of structures do not depend solely on the presence of P66 expression, as the Δp66 bacteria stimulate growth and structure formation by the endothelial cells, but to a lesser degree than do the wild-type bacteria. While in the bacterial infections, P66 was not the only determinant of endothelial cell growth, when purified proteins were tested in similar experiments, the integrin binding activity of P66 was critical (panels D and E). (D) P values in comparisons of purified maltose-binding protein (MBP)-P66 fusion proteins and control proteins in comparisons to VEGF and no additions (positive and negative controls, respectively). βgal, β-galactosidase. (E) Integrin αIIbβ3 binding activity of MBP-P66 carrying site-directed changes to two aspartic acid residues in the previously identified integrin-binding domain. E. coli never resulted in structure formation or endothelial cell growth but did kill the cells within 3 days regardless of the presence or absence of Matrigel (not shown).