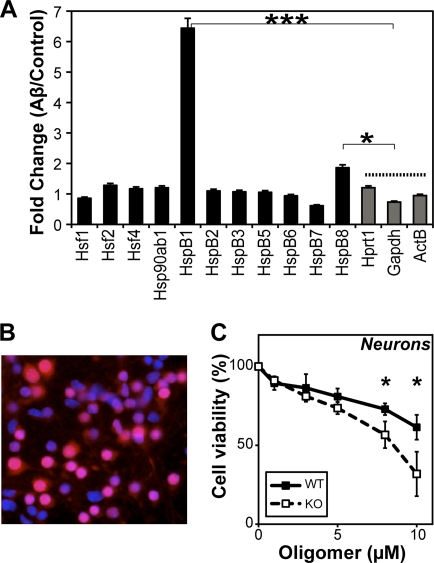
Fig. 6.
Importance of cellular HspB1 in Aβ toxicity. (A) Fold change in the expression of sHsps (7 out of 10 homologs, HspB1, -2, -3, -5, -6, -7, and -8), heat shock transcription factors (Hsf1, Hsf2, and Hsf4), Hsp90ab1, and housekeeping genes (Hprt1, GAPDH, and ActB) as monitored by reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR). N2a cells were treated with Aβ oligomers (10 μM as monomers) for 1 h, after which Aβ was removed by replacing the medium. Cells were incubated in serum-rich medium for an additional 2 h, and RNA was extracted. As control, cells were treated identically but without Aβ addition. Fold changes in gene expression between Aβ-treated and control cells were plotted. Data were compared against those for the housekeeping genes by two-sample t test, and asterisks indicate statistically significant differences. (B) Representative preparation of primary mouse cortical neurons showing an overlay of staining for neuronal marker NeuN (red) and DAPI (blue). Magenta indicates neurons. (C) The toxicity of various concentrations of Aβ oligomers was tested on wild-type (WT) or HspB1-deficient (KO) neurons. Cell viability was measured by CellTiter Blue assay. Data were compared by two-sample t test, and asterisks indicate statistically significant differences.