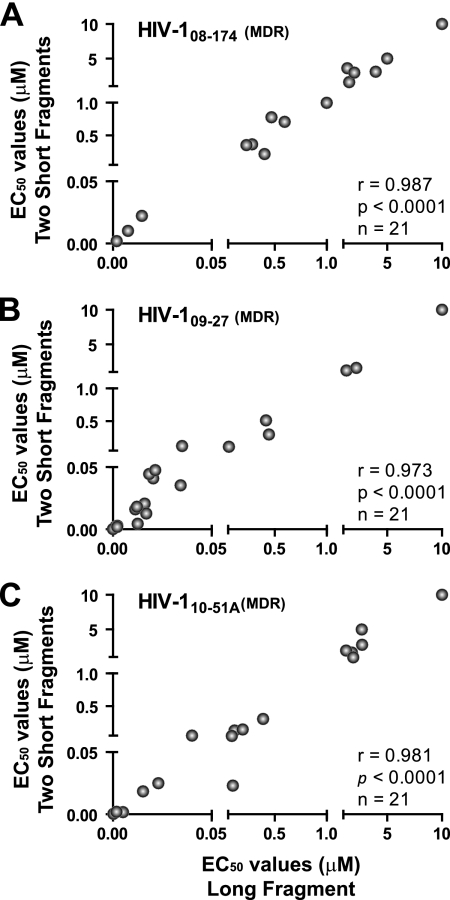
Fig. 2.
Drug susceptibility of three sets of p2-INT-recombinant viruses constructed using one large fragment (3,428 nt) or two short overlapping (1,657 nt and 2,002 nt) fragments. PCR products were obtained from three treatment-experienced patients, 08-174 (A), 09-27 (B), and 10-51A (C), and cloned as described in Materials and Methods. Pearson correlation coefficient was used to determine the strength of association between the EC50s calculated with recombinant viruses generated with one large and two overlapping PCR products. Extreme reduced susceptibility to NVP (>50 μM), FTC (>100 μM), and 3TC (>300 μM) for the 08-174 virus and FTC (>100 μM) and 3TC (>300 μM) for the 09-27 and 10-51A viruses was converted to 10 μM for graphical purposes. Mutations associated with reduction in drug susceptibility for each virus included the following: 08-174 (in PR, L10I, I47IV, I50IV, I54A, A71V, G73S, I85V, L89V, and L90M; in RT, M41L, E44D, D67N, T69D, V75M, L100I, K103N, V118I, M184V, L210W, T215Y, and K219N; in INT, N155H); 09-27 (in PR, L10V and L90M; in RT, V118I, M184V, and P225H; in INT, N155H); 10-51A (in PR, L10V, V11I, L33F, M46I, I54M, A71V, V82F, and L90M; in RT, M41L, D67G, T69N, K70R, L74I, V75I, M184V, G190A, T215F, and K219Q; in INT, none). MDR, multidrug-resistant virus; r, correlation coefficient; P, two-tailed P value; and n, number of drugs analyzed per set of recombinant viruses. EC50s represent the mean of three independent measurements.