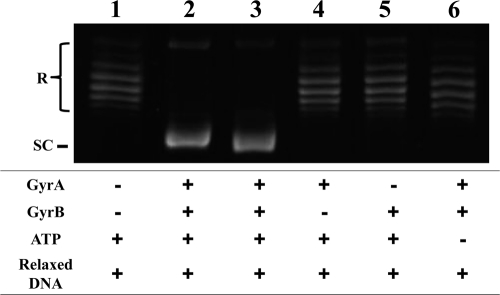
Fig. 2.
Recombinant WT GyrA and GyrB subunits of M. tuberculosis generate an ATP-dependent DNA supercoiling activity. Relaxed pBR322 DNA (0.3 μg) was incubated with WT DNA gyrase reconstituted from GyrA (3 μM) and GyrB (3 μM) in the presence and absence of 1 mM ATP. The reactions were stopped, and the DNA products were separated by electrophoresis in 1% agarose gels. DNA was stained with ethidium bromide and photographed under UV illumination. Lane 1, relaxed pBR322 DNA; lane 2, relaxed pBR322 DNA and E. coli DNA gyrase; lane 3, relaxed pBR322 DNA and both recombinant GyrA and GyrB proteins; lane 4, relaxed pBR322 DNA and only GyrA protein; lane 5, relaxed pBR322 DNA and only GyrB protein; lane 6, absence of ATP. R and SC, relaxed and supercoiled pBR322 DNA, respectively.