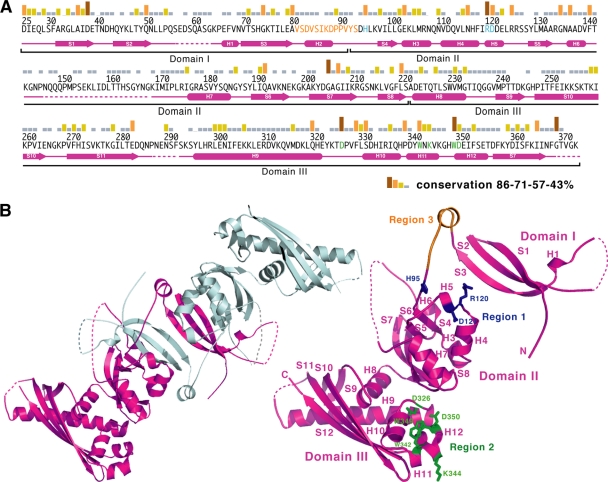
Fig. 1.
Sequence conservation between B. subtilis GerBC and its homologs in Bacillales species. (A) Amino acid sequence of the B. subtilis GerBC protein. Sequence conservation among the 109 GerBC homologs in the Bacillales is shown as a bar graph. Secondary-structure assignments of GerBC (10) are shown as magenta cylinders (α helices) and arrows (β strands), while disordered regions are shown as broken lines. The amino acid residues that are mutated in this work are shown in blue (region 1), green (region 2), and orange (region 3). (B) Overview of the interlocked dimeric B. subtilis GerBC structure (10) (left) and the location of the mutated regions in the GerBC monomer structure (right). The two monomers of GerBC are colored in magenta and grey. The residues that are mutated in regions 1 and 2 are shown as ball-and-stick models and are colored as in panel A. The residues deleted in region 3 are also colored in orange.