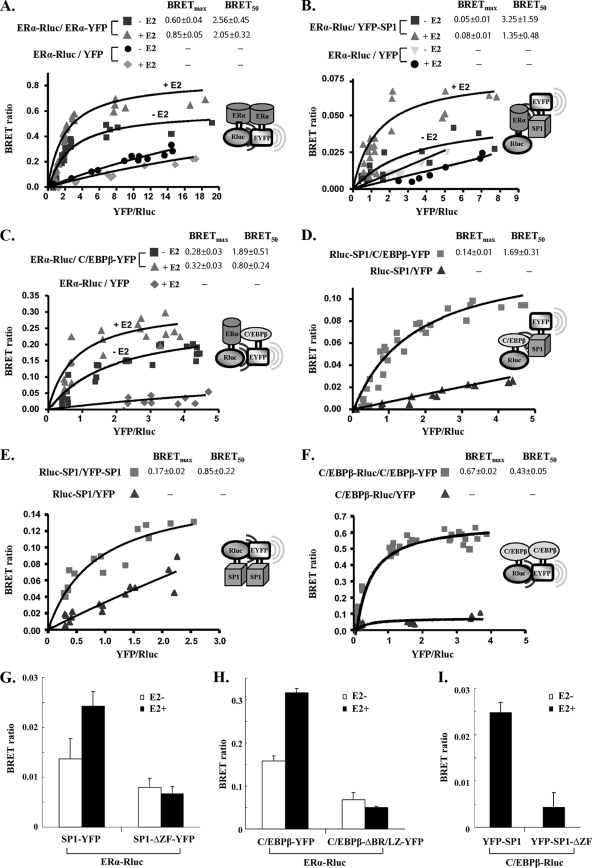
Fig. 6.
Interactions of ERα-ERα, ERα-C/EBPβ, ERα-SP1, SP1-C/EBPβ, SP1-SP1, and C/EBPβ-C/EBPβ in living mammalian cells. A fixed amount of plasmids for Rluc-tagged donor (0.2 μg of ERα-Rluc, Rluc-SP1, or C/EBPβ-Rluc) was cotransfected into COS1 cells with the following increasing doses of YFP-tagged acceptor plasmid: ERα-YFP of 0.025 to 1 μg with ERα-Rluc (A); YFP-SP1 of 0.1 to 0.8 μg with ERα-Rluc (B); C/EBPβ-YFP of 0.1 to 0.8 μg with ERα-Rluc (C); C/EBPβ-YFP of 0.05 to 1 μg with Rluc-SP1 (D); YFP-SP1 of 0.05 to 2 μg with Rluc-SP1 (E); and C/EBPβ-YFP of 0.05 to 2 μg with C/EBPβ-Rluc (F). In all cases, YFP alone as the acceptor together with the respective Rluc fusion plasmid as the donor were used as the negative control. BRET levels were plotted as a function of the ratio of the expression level of the YFP construct to the Rluc construct (YFP/Rluc). BRETmax, the maximal BRET ratio obtained for a given pair; BRET50, relative affinity of the acceptor/donor ratio required to reach a half-maximal BRET value. (G to I) The BRET ratio was determined when fixed amounts of ERα-Rluc (0.1 μg) (G and H) or C/EBPβ-Rluc (0.1 μg) (I) were cotransfected into COS1 cells with the YFP-tagged wild type (0.2 μg) or corresponding mutant (0.2 μg). SP1-ΔZF-YFP, zinc finger motif-deleted mutant; C/EBPβ-ΔBR/LZ-YFP, basic region and leucine zipper-deleted mutant. Data are expressed as means ± standard deviations from four independent assays.