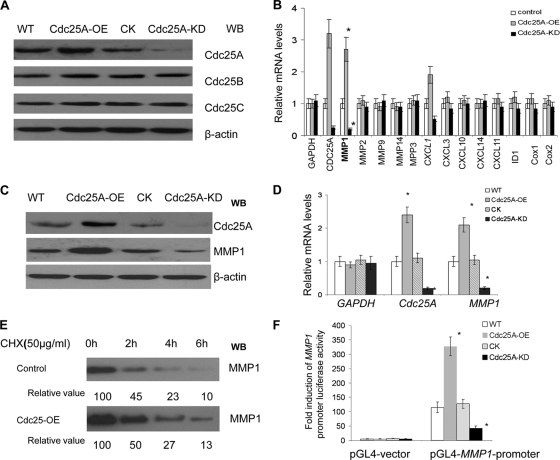
Fig. 1.
Cdc25A correlates with expression of metastasis factor MMP1. (A) Cdc25A was effectively and specifically overexpressed (Cdc25A-OE) or knocked down (Cdc25A-KD) in breast cancer cells. The controls Cdc25B and Cdc25C were intact in these cells. Our preexperiments showed no difference between the cells with pLenti-scramble-siRNA and those with empty pLenti-expressing vector (Invitrogen) that harbor the same pLenti vector base. Thus, either of them could serve as the control Cdc25A-CK. WB, Western blotting. (B) The relative mRNA expression levels of the metastasis-related factors were evaluated in the MDA-MD-231 breast cancer cell line and its derivatives Cdc25A-OE (overexpression) and Cdc25A-KD (knockdown) by quantitative real-time PCR; human GAPDH served as a loading control. These data represent three independent experiments (*, P < 0.01; means ± standard deviations [SD]; n=5). (C) Detection of MMP1 protein levels in breast cancer cells versus their derivatives Cdc25A-OE and Cdc25A-KD. (D) Evaluation of human Cdc25A and MMP1 mRNA levels in different breast cancer cells by qRT-PCR. Human GAPDH served as a loading control (*, P < 0.01 compared with the CK or WT; means ± SD; n=5). (E) Degradation rates of MMP1 protein in breast cancer cells. Exponentially proliferating cells were treated with 50 μg/ml cycloheximide (Chx) for the times indicated, and cellular MMP1 levels were determined by Western blotting. The data represent three independent experiments. (F) The pGL4-MMP1-promoter and the control pGL4 vector were transfected into the breast cancer cell line and its derivative Cdc25A-CK, Cdk25A-OE, or Cdc25A-KD, and fold induction of MMP1 promoter-induced luciferase activity was analyzed (*, P < 0.001 compared with the control or WT cells; mean ± SD; n=5).