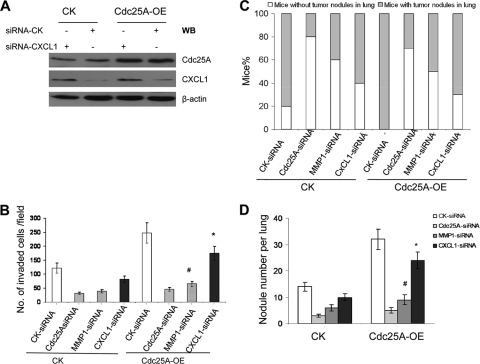
Fig. 12.
Comparison of the effects of CXCL1 knockdown or MMP1 knockdown on invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells driven by Cdc25A overexpression. The relative mRNA data (Fig. 1B) seem to indicate that CXCL1 is regulated by modulation of Cdc25A, as well, but these effects are weaker than that of Cdc25A on MMP1. To confirm and measure the contributions of MMP1 and CXCL1 in breast cancer cell metastatic phenotypes mediated by Cdc25A, we performed further assays. (A) CXCL1 protein levels in the indicated breast cancer cell line and its derivative with Cdc25A-OE were detected by Western blotting. (B) Cell invasion assay on Matrigel-coated Transwells and statistical analysis of cell invasive ability. The migrated cells were counted per high-power field (×200; 10 random fields). #, P < 0.01, and *, P < 0.1 compared to the CK-siRNA control in the Cdc25A-OE cells. The error bars indicate standard deviations. (C and D) The number of mice with metastasis (C) and tumor nodules in the lung (D) of the mice injected with the different breast cancer cells via the tail vein. The lungs and the H&E staining of metastatic tumors in the lungs were similar to those in shown in Fig. 5B and C. The nodules per lung for all 4 sections were counted under a light microscope. #, P=0.015, and *, P=0.21, compared to the CK-siRNA control cells and Cdc25A-OE cells; n=10. Similar results were observed in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-453 breast cancer cells versus their derivatives. The results showed that CXCL1 may play a small role in mediating the link between Cdc25A and the metastatic phenotypes. In contrast, MMP1 is a major factor in mediating the connection between Cdc25A and breast cancer metastasis.