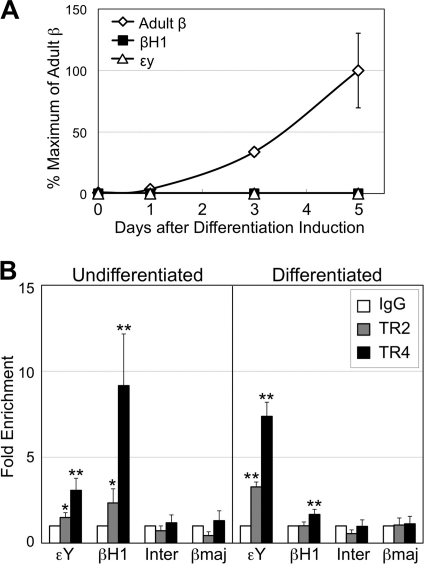
Fig. 1.
TR2/TR4 bind to the murine embryonic β-type globin gene promoters in adult erythroid (MEL) cells during differentiation. (A) Accumulation of murine adult β-globin transcripts (total of βmajor- and βminor-globin mRNAs), determined by reverse transcription and real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR), in MEL cells during differentiation induced by 2% DMSO. (B) Binding of TR2 and TR4 to the proximal promoter regions, including the DR sequences, of the murine embryonic εY- and βH1-globin genes in undifferentiated or differentiated MEL cells was analyzed by ChIP assay. The statistical significance of TR2 or TR4 enrichment at the embryonic globin promoters compared to control IgG values is indicated with asterisks (*, P < 0.08; **, P < 0.04 [Student t test]). For negative controls, the proximal promoter of the adult βmajor-globin gene (βmaj; which has no DR sequence), as well as an intergenic DNA segment (Inter) lying between the βH1 and βmajor genes (5.9 kbp 5′ to the βmajor promoter), was also analyzed. Error bars represent standard errors of the mean (SEM).