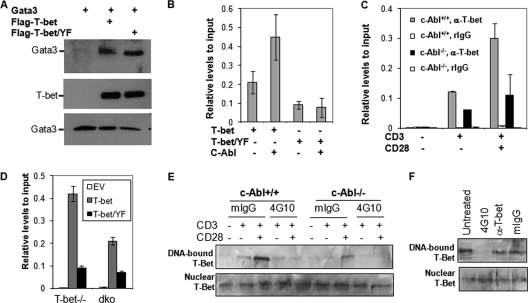
Fig. 5.
c-Abl-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation regulates T-bet DNA binding. (A) c-Abl-mediated phosphorylation does not affect T-bet interaction with GATA-3. T-bet, GATA-3, and c-Abl expression plasmids were cotransfected into HEK 293 cells as indicated. The interaction of T-bet with GATA-3 was analyzed by immunoprecipitation of T-bet and Western blotting detection of GATA-3 (top panel). The same membrane was reprobed with anti-T-bet antibody (middle panel). The expression of GATA-3 in the whole-cell lysates was detected as controls (bottom panel). (B) Jurkat T cells were transfected with expression plasmids for Flag-tagged T-bet or its Y220/226/305F mutant (T-bet/YF) in the presence or absence of c-Abl. The binding of T-bet and its YF mutant to IFN-γ promoter was analyzed by ChIP assay with anti-Flag antibody followed by real-time PCR analysis. (C) Primary CD4+ T cells from c-Abl+/+ and c-Abl−/− mice were stimulated with anti-CD3 plus anti-CD28 for 24 h. Stimulated cells were subjected to ChIP assay using anti-T-bet antibody, and the binding of T-bet to IFN-γ promoter DNA was analyzed by real-time PCR. ChIP analysis with normal rabbit IgG (rIgG) was performed as a negative control. (D) Primary T cells from T-bet−/− and T-bet/c-Abl double-knockout (dko) mice were infected with retrovirus that carries T-bet or Tbet/Y220/266/305F (T-bet/YF). Infected cells were subjected to ChIP analysis with anti-T-bet antibody. Error bars represent data from three independent experiments (average ± standard deviation). EV, empty vector. (E) Nuclear extracts from total T cells from c-Abl+/+ and c-Abl−/− mice upon TCR/CD28 stimulation were isolated and incubated with 1 μg antiphosphotyrosine antibody (4G10) or with 1 μg control normal mouse IgG (mIgG) for 30 min. An oligonucleotide pulldown assay was performed. The bound T-bet (top panel) as well as T-bet in nucleic extracts (bottom panel) was detected by Western blotting. (F) Nucleic extracts from stimulated wild-type T cells were incubated without (Untreated) or with mIgG, 4G10, or anti-T-bet Abs (1 μg each), and an oligonucleotide pulldown assay was performed as described for panel E.