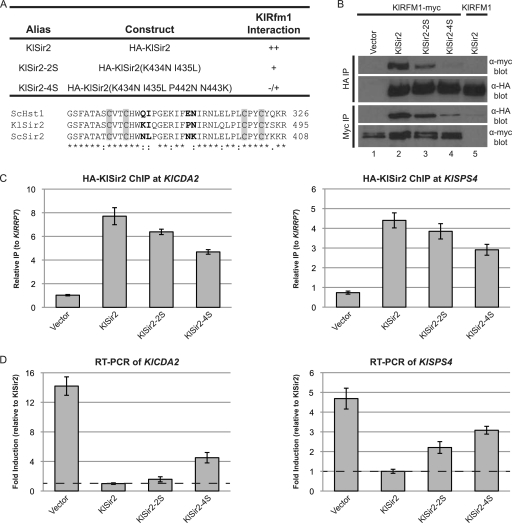
Fig. 5.
The interaction domain for Rfm1 is conserved between KlSir2 and ScHst1. (A) Summary of mutations and their properties. An alignment of the zinc-binding domains of ScHst1, KlSir2, and ScSir2 is shown, with mutated residues in bold and the zinc-binding cysteines in gray boxes. (B) The association of KlSir2 with KlRfm1 was examined by co-IP. HA-KlSir2 or KlRfm1-myc was immunoprecipitated from a Klsir2Δ KlRFM1–myc mutant strain (LRY2654) transformed with an empty vector (pLR849) or plasmids expressing the constructs shown in panel A or a Klsir2Δ mutant strain with untagged KlRFM1 (LRY2128) transformed with HA–KlSIR2. (C) The association of HA-KlSir2 with the promoters of KlCDA2 and KlSPS4 was assessed by ChIP using the same strains as in panel B. Enrichment at the promoters is expressed relative to the KlRRP7 locus, which is not associated with KlSir2. (D) Expression of KlCDA2 (KLLA0C17226g) and KlSPS4 (KLLA0F08679g) was assessed by RT-PCR in the same strains as in panel B. Levels of KlCDA2 and KlSPS4 mRNA were first normalized to KlACT1 and then expressed relative to those of the strain containing wild-type HA-KlSir2.