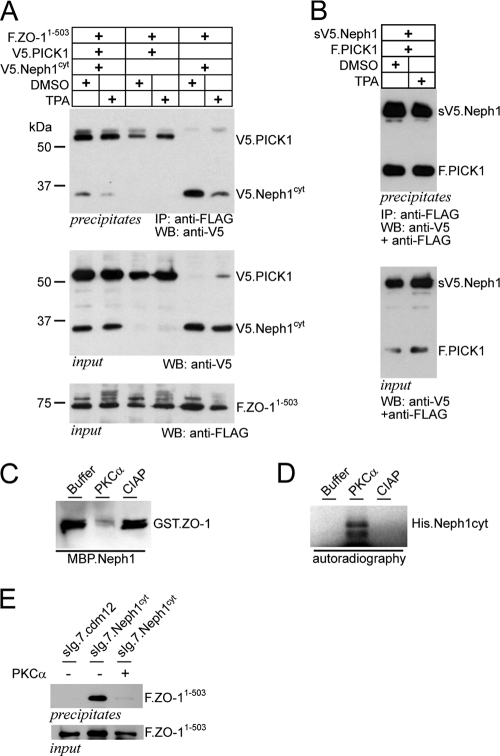
Fig. 5.
PKCα and PICK1 cooperatively regulate the Neph1/ZO-1 plasma membrane complex. (A) FLAG-tagged ZO-11–503 and V5-tagged Neph1cyt were coexpressed with PICK1 or empty vector. ZO-1 was precipitated with anti-FLAG antibody. Western blot analysis was performed with a V5-specific antibody to detect coprecipitated Neph protein. Activation of protein kinase C (PKCα) with 200 nM PMA inhibits the interaction (lane 5 and 6). Coexpression of PICK1 further augments the PKC effect on the Neph1/ZO-1 interaction (lane 1 and 2) without affecting protein levels (middle and lower panels). (B) PMA does not influence the PICK1/NEHP1 interaction. Experimental setting as in panel A with the constructs indicated. (C and D) The interaction Neph1/ZO-1 is regulated through PKCα activity. (C) Pulldown assay of bacterially expressed GST.ZO-11–111 and MBP.Neph1cyt in the presence of buffer, PKCα, or calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (CIAP). Addition of PKCα abrogates the Neph1/ZO-1 interaction, whereas CIAP did not affect the interaction. (D) Kinase assay of bacterially expressed His.Neph1cyt in the presence of radioactively labeled ATP and buffer, PKCα or CIAP. Addition of PKCα led to phosphorylation of Neph1cyt. Autoradiograph after in vitro phosphorylation of His.Neph1cyt (E) Membrane-bound Neph1cyt (sIg7.Neph1cyt) or a control plasmid (sIg.7.cdm12) and FLAG-tagged ZO-11–503 were expressed in HEK 293T cells and precipitated with protein G. Western blot analysis was performed with a FLAG-specific antibody. Overexpression of PCKα abrograted the Neph1/ZO-1 interaction.