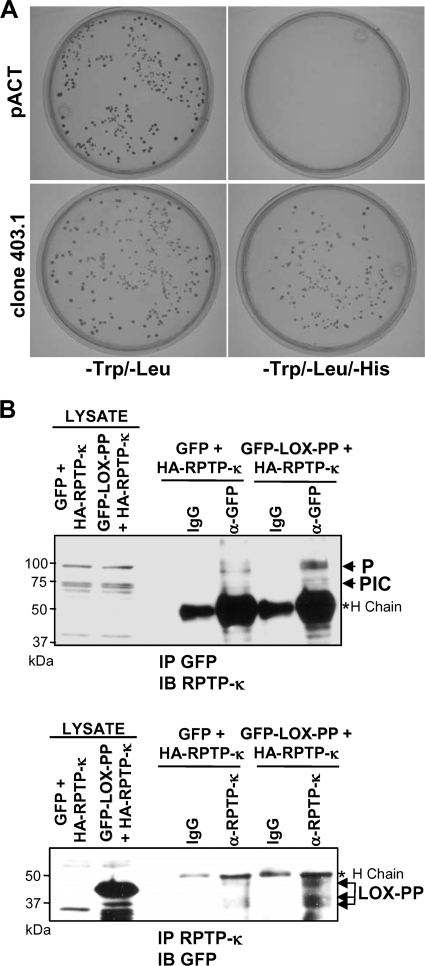
Fig. 1.
LOX-PP interacts with RPTP-κ in yeast and mammalian cells. (A) Yeast AH109 cells expressing LOX-PP were transformed with an empty library vector (pACT) or the RPTP-κ library clone 403.1. Transformants were plated in minimal medium (−Trp/−Leu or −Trp/−Leu/−His) to probe for expression of the reporter genes. (B) HEK 293T cells were transfected with an HA-tagged RPTP-κ expression plasmid (3 μg) in combination with 3 μg of vectors expressing either GFP (control) or GFP-LOX-PP. After 48 h, whole-cell lysates (200 μg) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with an antibody directed against either GFP (α-GFP, upper panel) or RPTP-κ protein (α-RPTP-κ, lower panel) or control IgG (IgG). The immunoprecipitated (IP) proteins and samples of lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE. The resulting immunoblots (IB) were analyzed using an antibody against RPTP-κ (IP GFP, IB RPTP-κ, upper panel) or GFP (IP RPTP-κ, IB GFP, lower panel). Positions of the precipitated ∼95-kDa P subunit, ∼70-kDa PIC subunit, and LOX-PP proteins are indicated. For estimation of the amounts of expressed proteins, 17% of each of the lysates was separated and immunoblotted (LYSATE lanes).*H chain, immunoglobulin heavy chain. The positions of molecular mass markers are given on the left.