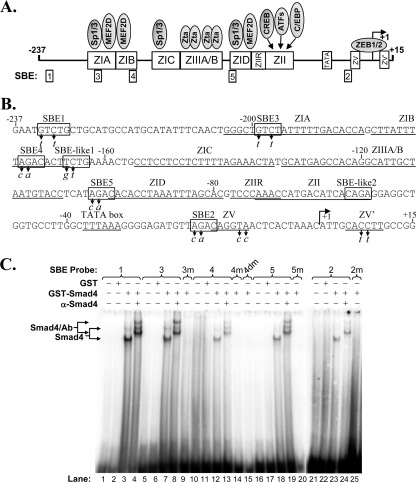
Fig. 4.
Identification of novel Smad-binding elements within Zp. (A) Schematic diagram indicating cis-acting elements present within the nt −237 to +15 region of Zp relative to the transcription initiation site. Rectangles along Zp indicate approximate locations of regulatory elements with their known trans-acting factors indicated above them and SBEs indicated below. (B) Sequence of the nt −237 to +15 region of Zp. SBEs are indicated within rectangles. The base pair substitution mutations (m) in the SBEs studied here are indicated by italicized letters below the wild-type sequence. Locations of the previously reported cis-acting Z elements are indicated by lines below the sequence. The transcription initiation site is indicated by a rightward arrow. (C) EMSAs showing binding of Smad4 to SBEs. EMSAs were performed with the indicated radiolabeled double-stranded oligonucleotides (8 ng) as probes. Purified GST-Smad4 or GST (120 ng) was used as indicated as the protein source. Immunoshift assays were performed with 2 μg of antibody specific to Smad4. Locations of the protein/DNA complexes are indicated.