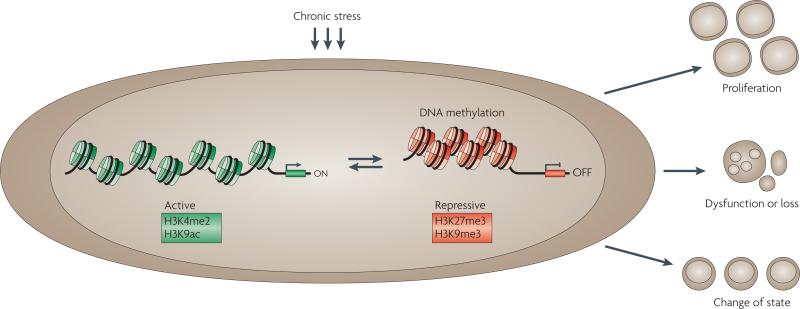
Figure 2. Perturbations caused by chronic stress.
Chronic stress may result in epigenetic changes. For example, alterations in DNA methylation, histone modifications and nucleosome positioning might occur. In the example shown, the changes result in gene silencing. The epigenetic changes may result in heritable patterns of altered gene expression that result in abnormal cell states: proliferation, dysfunction or loss, or a change of state. Such changes can contribute to disease, as discussed in the text. The histone modifications shown here associated with active transcription are histone H3 lysine 4 dimethylation (H3K4me2) and H3 lysine 9 acetylation (H3K9ac); the modifications associated with transcriptional repression are H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) and H3 lysine 9 trimethylation (H3K9me3).